Have you ever wondered how doctors at different hospitals manage to share your health records so quickly? That’s thanks to healthcare interoperability. It’s basically about making sure all the technology used in healthcare—from the computers at your local clinic to the big systems in hospitals—can talk to each other effectively.
This guide will walk you through what interoperability really means in healthcare, why it’s super important, and how it helps everyone from doctors to patients. We’ll also touch upon some healthcare interoperability challenges that come with it and how AppStudio is helping to make things smoother. So, let’s get started!
What is Interoperability in Healthcare?
To define interoperability in healthcare, it is the ability of diverse healthcare information systems—such as Electronic Health Records (EHRs), lab systems, and imaging software—to connect, exchange data, and function cohesively. The aim is to establish a cohesive, efficient, and patient-focused healthcare environment.
Within this system, healthcare professionals like doctors, nurses, and pharmacists can quickly and securely access and share a patient’s medical records, no matter where the care was provided or the specific systems used by the healthcare providers.
Related reading: Top 10 Mobile App Features in Healthcare
What Data is Exchanged Via Interoperable Healthcare Systems?
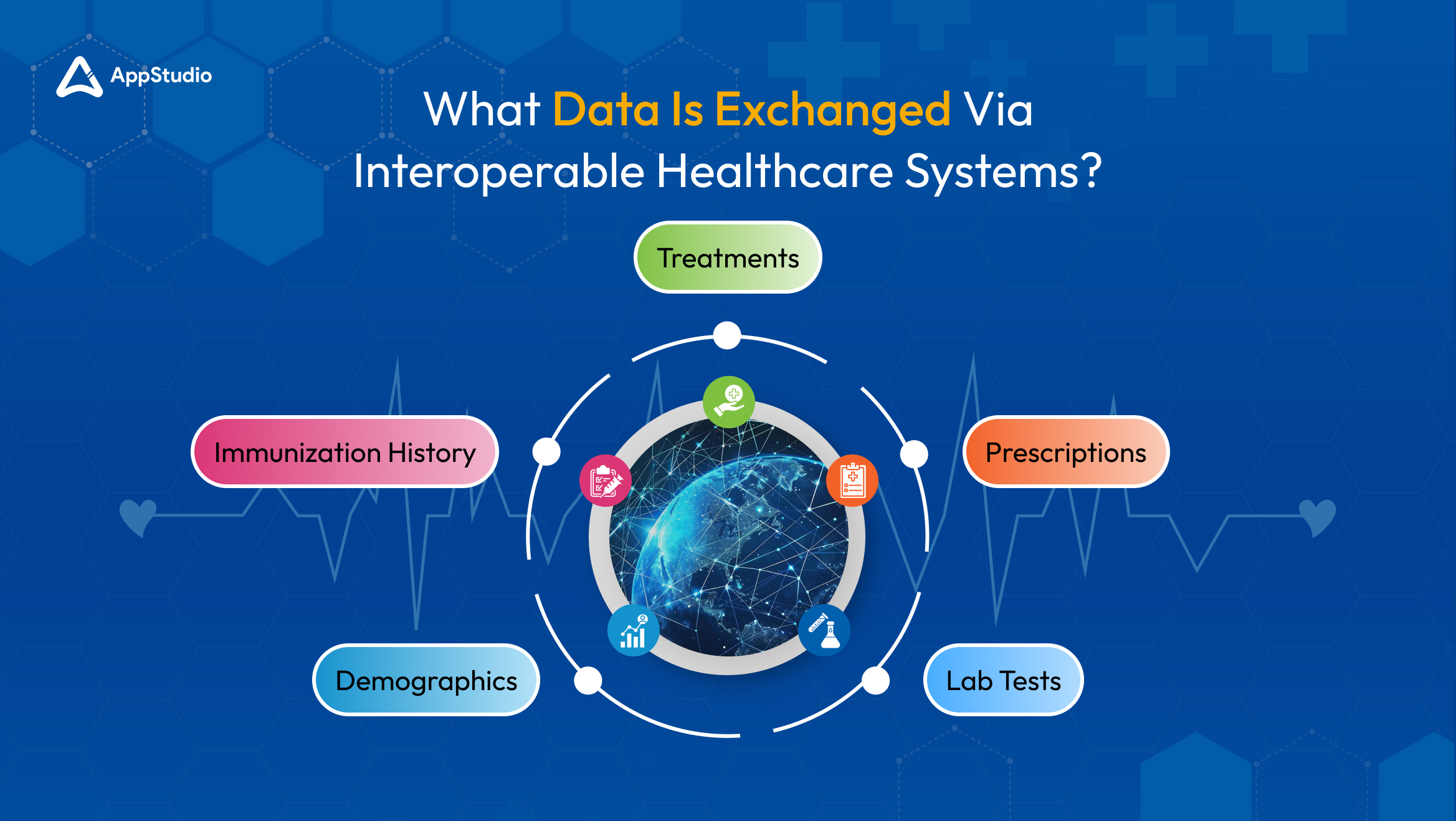
Interoperable healthcare systems share various types of patient data, such as details about treatments, prescriptions, lab tests, demographics, and immunization history. Patients often expect that this information will be easily accessible. However, healthcare leaders and government officials aim to expand the data shared to include more specific demographic details (like ethnicity and primary language), genetic information, allergies, and communications from healthcare providers.
The US Department of Health and Human Services suggests that standardizing the collection of comprehensive data, including lifestyle choices like diet and smoking habits, could highlight health inequalities and enable healthcare providers to tailor interventions more effectively.
Benefits of Interoperability in Healthcare
So far you would have understood what interoperability in healthcare facilitates, now, let’s break down the benefits of it.
Improved Patient Care
Access to complete medical records helps doctors make better decisions about patient care. When doctors have a full view of a patient’s health history, they can diagnose more accurately and plan treatments that fit the patient’s specific needs and lifestyle. For example, if a patient visits different specialists, each specialist can see the patient’s entire treatment history. This helps them avoid repeating the same tests or prescribing medicines that might clash with what others have prescribed.
Cost Reduction
One of the key benefits of interoperability in healthcare is cost reduction. The frictionless exchange of data cuts down on unnecessary tasks and paperwork. You won’t have to repeat tests or scans because you can quickly look up past results, saving both time and money. This reduction in repeated tests and manual data entry helps healthcare systems lower their operating costs.
Enhanced Patient Safety
Having real-time access to detailed health records helps healthcare providers manage medications and treatments more safely. If a patient has allergies or adverse reactions to certain medications, these details are readily visible to all healthcare professionals they encounter. This, in turn, prevents potential medical errors.
Better Public Health Reporting and Monitoring
Efficient data collection and analysis via interoperable systems is crucial for monitoring public health issues and managing outbreaks. For instance, during an infectious disease outbreak, real-time data can track the spread and effectiveness of response strategies, allowing for rapid adjustments.
Improved Healthcare Data Security
While interoperability allows for broader sharing of patient information, it’s essential to clarify that enhanced security measures are crucial to protect this data. Strong protocols and regulations, such as HIPAA in the U.S., help safeguard patient information from unauthorized access, but risks can still exist if systems are not properly managed.
Accelerated Innovation
A standardized, interoperable framework allows developers and researchers to work together more efficiently to create new tools. Since they’re using a common set of rules, they can concentrate on developing specific applications instead of building everything from scratch. This speeds up the creation of advanced tools for analyzing data, telehealth systems, and AI-driven diagnostic tools, among other innovations.
Related reading: Software Architecture for Healthcare Apps in 2024
Four Levels of Data Interoperability in Healthcare
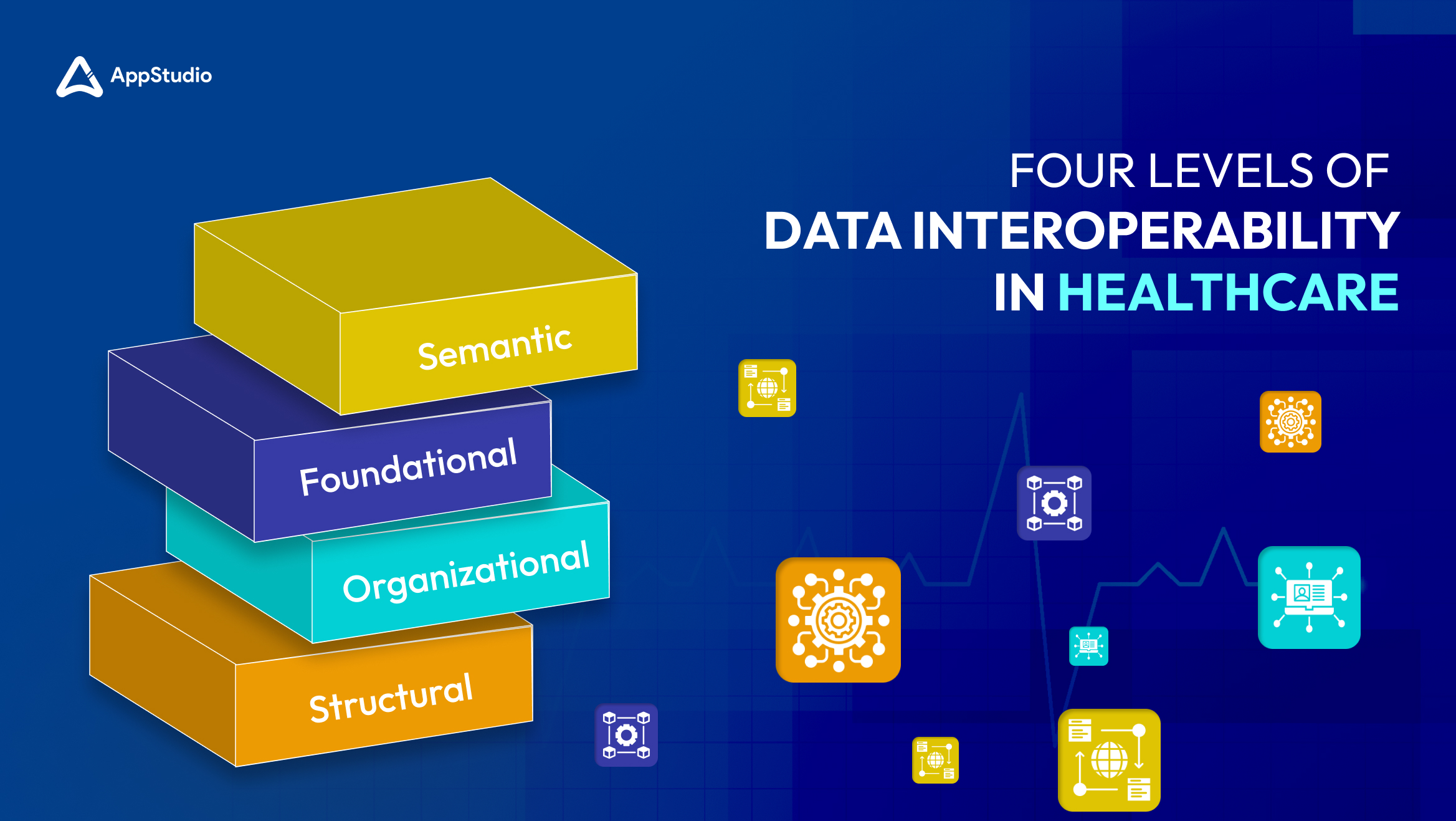
Interoperability solutions in healthcare involve different levels that help systems and devices communicate effectively. These levels are outlined by informatics experts and the Healthcare Information and Management Systems Society (HIMSS). Each level addresses different capabilities of healthcare IT systems, from basic data exchange to complex integrated uses. Here’s a simple breakdown of these levels:
Foundational Interoperability
What it is: This is the most basic level of interoperability. At this stage, data moves from one system to another without any modification.
Example: Think of a nurse downloading a patient’s lab results as a PDF from a lab’s portal and then entering that data into the health record manually. The data is simply moved and not changed or interpreted.
Structural Interoperability
What it is: At this level, data is not only exchanged but also organized in a standard way that allows different systems to understand and use the data automatically.
Example: If a patient’s record is sent from one hospital to another, the receiving system recognizes and places the data in the correct fields automatically, thanks to common data formats like FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources) or HL7 (Health Level Seven International).
Semantic Interoperability
What it is: This is a more advanced form of interoperability. Data can be exchanged between systems that use different ways to store information. The systems not only receive data but can also interpret it correctly.
Example: An MRI image saved in a specific format in one hospital’s system can be sent to and used by another hospital’s different system without any confusion about what the image shows.
Organizational Interoperability
What it is: This level involves the coordination and collaboration between different healthcare organizations. It ensures that data sharing supports broader healthcare goals across various systems and practices.
Example: Different healthcare providers, insurance companies, and regulatory bodies share and use data efficiently while respecting privacy laws and regulations.
Related reading: How is IoMT Revolutionizing the Healthcare Industry?
The Challenges of Interoperability in Healthcare
Many healthcare experts and leaders believe that improved interoperability would greatly enhance healthcare. However, healthcare organizations encounter several common challenges as they strive to make their data and systems more interoperable. Let’s look at these challenges and discuss ways to address them:
Coordinating Efforts Across Organizations
To improve interoperability, there needs to be strong coordination not only between different healthcare organizations, but also among regulators and leaders within those organizations. To address this, organizations should develop a dedicated strategy for interoperability and prioritize its implementation.
Budget Constraints
Many healthcare organizations may not have sufficient money or technical resources to develop fully interoperable systems. However, they might be eligible for government grants to upgrade their health records systems. Additionally, some cloud vendors offer pay-as-you-go pricing, which can help make the costs more manageable.
Varying Technology Requirements
Different healthcare providers must adhere to specific regulations based on their location and the services they offer, leading to highly customized data systems. One solution is to use hybrid cloud platforms, which allow organizations to merge and manage their data efficiently without losing necessary customizations.
Updating Old Systems
Healthcare organizations often use older systems that aren’t built for modern interoperability standards. To tackle this, they can use a hybrid cloud strategy to pull data from these old systems and use it in more modern applications. This method allows them to update their processes gradually, while keeping the data flow intact.
Related reading: Imperative Role of Cloud Computing in the Healthcare Industry
How AppStudio Can Help with Healthcare Interoperability

AppStudio collaborates with healthcare organizations to develop and implement effective interoperability strategies. We ensure clear goals, timelines, and budgets are set, aligning all stakeholders for smooth implementation.
Our financial and technical solutions are designed to be cost-effective, meeting the budgetary needs of healthcare providers and leveraging cloud technologies to enhance system integration without compromising on customizations or regulatory requirements.
AppStudio is adept at modernizing legacy systems to adhere to contemporary interoperability standards, thus ensuring uninterrupted and secure data flow. Our approach not only supports the seamless integration of old and new systems but also boosts operational efficiencies and improves patient care outcomes.So, are you ready to enhance your healthcare system’s interoperability? Reach out to AppStudio today to see how we can tailor our services to meet your needs.
Data Interoperability in Healthcare FAQs
Imagine a patient on vacation has a severe allergic reaction and is taken unconscious to a nearby hospital. If healthcare systems are fully interoperable, the emergency team could immediately access the patient’s full medical history from their primary care provider’s electronic health records (EHR), ensuring they receive informed care.
The interoperability in healthcare meaning refers to the capacity of various healthcare systems and devices to exchange and interpret shared data seamlessly, regardless of the manufacturers behind them.
Interoperability allows nurses to access comprehensive patient information effortlessly. For instance, a nurse could review a patient’s entire health history, including vaccination records, current medications, and details of past hospital visits, before even meeting the patient.
Major interoperability challenges in healthcare include the lack of standardization across different EHR systems, privacy concerns regarding patient data, and the technological and financial barriers that healthcare facilities face in upgrading their systems to support interoperability.
It ensures that no matter where patients go for care, their health information travels with them. This continuity of information can lead to better diagnosis, faster treatment, and reduced duplication of tests, ultimately saving time and costs for patients.