Many healthcare providers recognize the transformative potential of user friendly EHR interfaces and applications to streamline processes and centralize patient data. However, despite these benefits, certain challenges remain. A Stanford report shows that 74% of physicians report an increase in their overall working hours due to EHR usage, while 71% link these systems to a notable rise in burnout. Additionally, 69% mention that EHRs sometimes limit the time they can spend directly engaging with patients, which is central to quality care. Exhausting, right?
The good news is that a thoughtfully designed user friendly EHR interface can alleviate many of these common issues, simplify workflows, and create a more seamless experience. But what exactly does an intuitive, effective EHR interface look like?
In this article, we’ll share actionable insights for crafting a convenient and engaging EHR interface, combining best practices with AppStudio’s in-depth UI/UX expertise. So let’s begin.
What Does an EHR/EMR Interface Mean?
An EHR/EMR interface design refers to the visual layout and functional elements that enable healthcare providers to access, navigate, and manage electronic health record systems. It’s the critical interaction point through which users engage with various EHR/EMR system components, encompassing both visual elements and the underlying framework that connects multiple EHR/EMR features.
In broader terms, EHR/EMR interface design shapes the entire user experience by balancing aesthetics with utility. The design spans the appearance and functionality of the system, covering everything from intuitive navigation menus to clearly labeled icons and responsive layouts. Beyond the surface, a user friendly EHR interface is also a technical bridge. This bridge connects various components, often built by different vendors, creating a single, unified platform for providers. Given the diversity of tools and systems, this unified interface allows healthcare providers to perform tasks without switching between different applications or systems.
Since the core objective of an EHR system is to streamline communication and enhance teamwork among healthcare providers, the interface must incorporate a wide array of tools—such as:
- Appointment
- Scheduling
- Prescription management and
- Diagnostic tracking—all in one place.
This integration is vital to supporting clinical workflows, allowing different departments or providers to work together seamlessly.
Related reading: What is EHR System and How to Build It? – Guide and Process
Why is it Important to Design Simple EMR Interfaces?
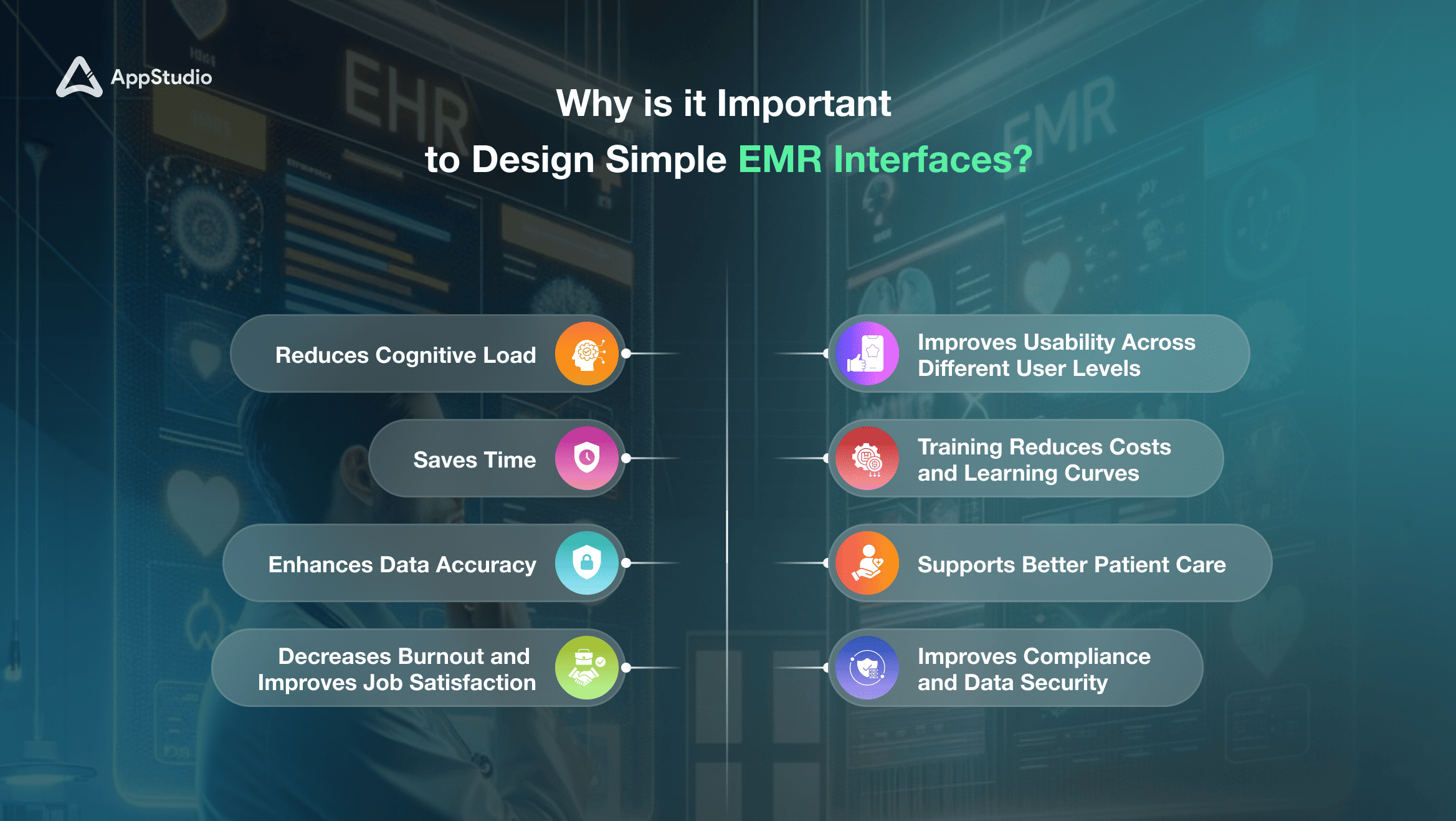
Creating a simple, intuitive EMR interface is essential for supporting the efficiency and well-being of healthcare providers. Here’s why simplicity in EMR design matters:
1. Reduces Cognitive Load
A clear and streamlined interface minimizes the mental effort required to navigate various functions. By reducing cognitive load, providers can focus more on patient care rather than on figuring out the software, resulting in fewer errors and faster task completion. Research indicates that healthcare providers can save up to 2 hours per day using efficient EMR systems, allowing them to concentrate more on patient interactions rather than administrative tasks.
2. Saves Time
Time is critical in healthcare. A straightforward EMR interface reduces the time needed to access, input, and retrieve information, enabling healthcare providers to attend to more patients in a day. This efficiency also reduces waiting times, improving patient satisfaction.
3. Improves Usability Across Different User Levels
A well-designed, simple EMR interface benefits users with varying levels of technical proficiency. Whether a user is tech-savvy or less comfortable with digital systems, an intuitive interface ensures everyone can navigate the system easily and without frustration.
4. Reduces Training Costs and Learning Curves
Simpler interfaces make learning faster, reducing the time and resources spent on training. This is particularly beneficial in healthcare facilities where turnover can be high, and new staff members must quickly familiarize themselves with the system. A study highlighted that users who received EMR training were 4 times more likely to be satisfied with the system than those who did not receive training.
5. Enhances Data Accuracy
A clear and simple interface lowers the chance of data entry errors, which can happen when users are overwhelmed by a cluttered, complex layout. Improved data accuracy leads to better patient records and reduces the risk of misdiagnoses or incorrect treatment plans.
6. Decreases Burnout and Improves Job Satisfaction
Complicated EMR systems can contribute to physician burnout. A simplified design reduces frustration, allowing providers to focus on their core responsibility—patient care—without being bogged down by administrative tasks. In 2023, statistics revealed that complicated EMR systems lead to 70% of physician burnout reporting health information technology (HIT)- related stress. This stress is particularly prevalent in primary care specialties, highlighting how inefficient software can hinder providers’ focus on patient care and increase administrative burdens.
7. Supports Better Patient Care
Ultimately, a simple yet a user friendly EHR or EMR interface allows healthcare providers to spend more time with patients and less time on the system. This added focus enhances the quality of care, as providers can address patient concerns without the distraction of complicated software navigation.
8. Improves Compliance and Data Security
Simpler interfaces with clear workflows reduce errors related to compliance and security. When interfaces are straightforward, users are less likely to skip necessary steps or overlook security protocols, helping the organization maintain data privacy standards.
Related reading: 10 Pros and Cons of Customizing Your EHR
14 Core Principles of a User-Friendly EMR System Interface
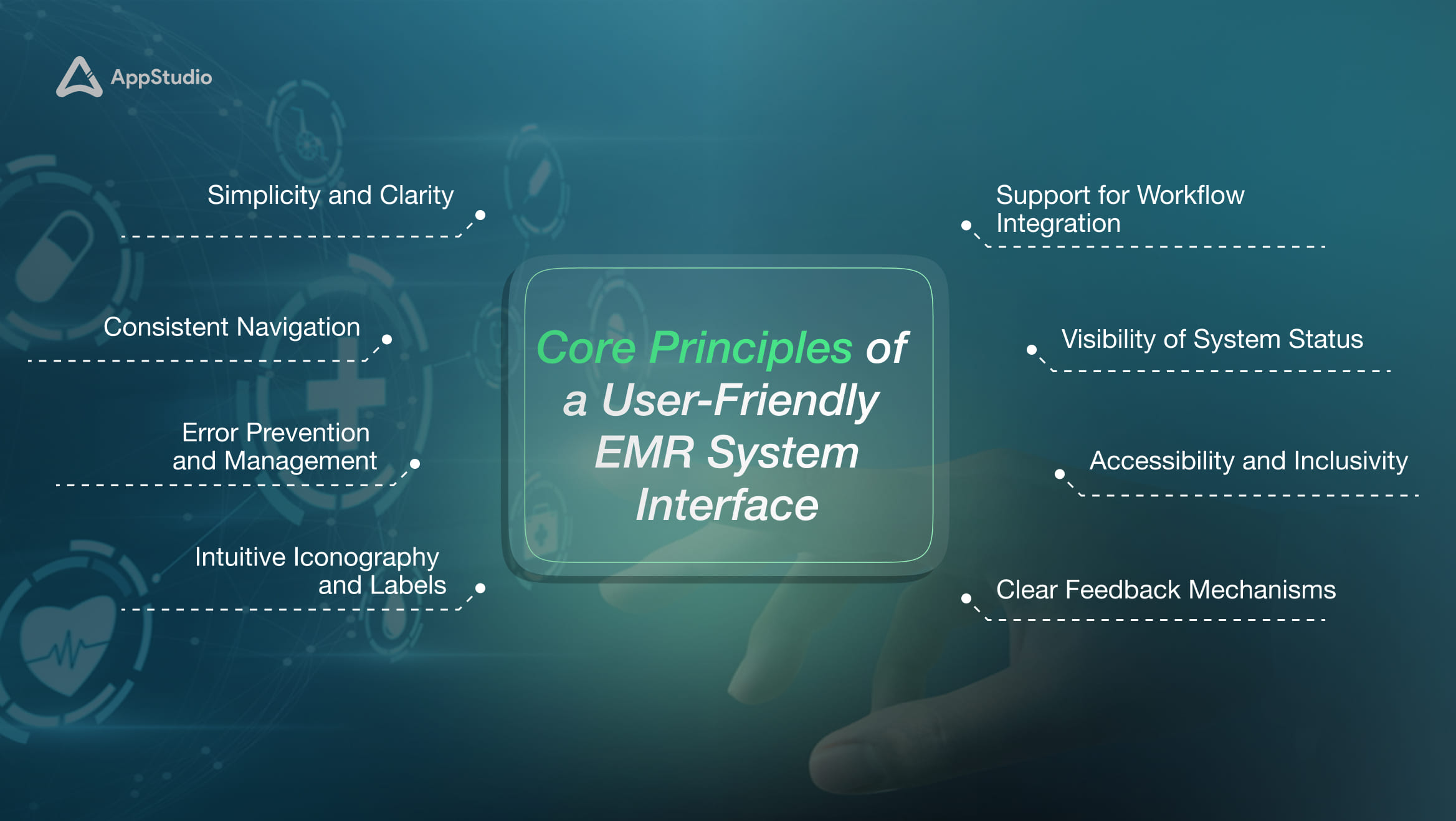
To create an effective and intuitive EMR interface, blending functionality with simplicity is essential, ensuring healthcare professionals can work efficiently. Here’s a detailed look at the EHR design principles that make an EMR interface truly worthwhile and aligned with the fast-paced needs of modern healthcare.
1. Simplicity and Clarity
A well-designed EMR interface displays only the most essential information, reducing distractions and preventing information overload. Users can quickly locate the necessary tools and information by emphasizing simplicity and clarity.
For example, a clean dashboard with a straightforward layout—such as color-coded icons for patient records, lab results, and appointments—lets users navigate with minimal clicks. Google’s Material Design is one such model for this approach, offering clean, intuitive visuals that streamline user experience across platforms.
2. Consistent Navigation
Consistency across the EHR interface promotes efficiency and reduces errors. When navigation is uniform, users don’t have to relearn layouts for different sections, making transitions smoother. A helpful approach is to design top-level menus and sidebars that remain visible throughout the interface, with standardized symbols and icons for routine tasks.
3. Minimal Cognitive Load
An EHR interface should guide users through essential actions without overwhelming them with unnecessary information. For instance, the interface supports easy comprehension by simplifying the visual hierarchy—highlighting key patient details and collapsing rarely used options.
4. Responsive Design
With healthcare providers using various devices, from desktops to tablets and mobile phones, a responsive EMR interface ensures accessibility across all platforms. Responsive design adapts the layout to fit different screen sizes without losing functionality.
5. Error Prevention and Management
Preventing errors is vital in healthcare, where mistakes can have severe consequences. Features like confirmation prompts before finalizing critical actions and error messages with guidance for resolution reduce mistakes.
6. Intuitive Iconography and Labels
Icons and labels should be universally recognized and intuitive. A magnifying glass icon for search, a home icon for the main dashboard, or a heart icon for patient vitals simplify navigation. Using recognizable icons reduces the learning curve for users, helping them operate confidently without the need for constant reference. For instance, most mobile and web applications leverage universal icons, making interfaces more accessible to a wider range of users.
7. Efficient Data Entry
Data entry should be streamlined to avoid redundancy and errors. Incorporating auto-complete templates and drop-down menus can significantly reduce time spent on repetitive tasks. For instance, in Athenahealth’s EHR, users can utilize customized templates for common procedures, expediting the documentation process while maintaining accuracy.
8. Support for Workflow Integration
The EMR interface should align seamlessly with clinical workflows. The design should facilitate transitions between tasks, from patient check-ins to diagnostics and treatment plans. For instance, if a doctor can directly access recent lab results or medication histories from a patient’s profile, it simplifies workflow. Systems like Epic offer integrated views for lab results, prescriptions, and appointments, keeping workflows uninterrupted and reducing the need for multiple steps.
9. Data Security
Given the sensitive nature of patient data, EMR interfaces must prioritize security. Features such as encrypted storage, two-factor authentication, and auto-logout enhance data protection. For example, the Mayo Clinic uses advanced encryption and multi-layered security for its EHR systems, ensuring patient information remains private and secure against unauthorized access.
10. Patient-Centric Focus
The design should make it easy for providers to access comprehensive patient information. A patient summary view, for instance, should allow quick access to recent treatments, medical history, and current medications, helping clinicians make informed decisions faster.
11. Visibility of System Status
Keeping users informed about system actions, such as loading screens or data saves, prevents confusion and duplicates actions. Visible indicators of system status improve trust and usability. For instance, Microsoft Azure’s interfaces display clear status updates for ongoing processes, which is equally useful in an EHR context to assure users of system performance.
12. Accessibility and Inclusivity
An inclusive design should accommodate healthcare professionals with diverse abilities. Features like screen readers, larger font options, and keyboard navigation make the interface accessible. For instance, Microsoft’s Accessibility Checker is widely used in healthcare to ensure that digital documents and interfaces meet inclusivity standards, allowing everyone to engage easily.
13. Customizable Layouts
Allowing users to personalize their EMR interface fosters comfort and efficiency. For example, a physician might keep recent patient files or commonly used tools readily available on their dashboard. In Cerner’s Millennium EHR, users can customize their interface based on their roles and preferences, which boosts productivity by putting essential features front and center.
14. Clear Feedback Mechanisms
Visual or audio feedback, such as a checkmark or a “success” notification, reassures users that actions have been registered. Feedback mechanisms reduce user uncertainty and errors.
Related reading: Top 10 EHR Features and Their Impact on Healthcare
Best EMR/EHR Interface Design Techniques
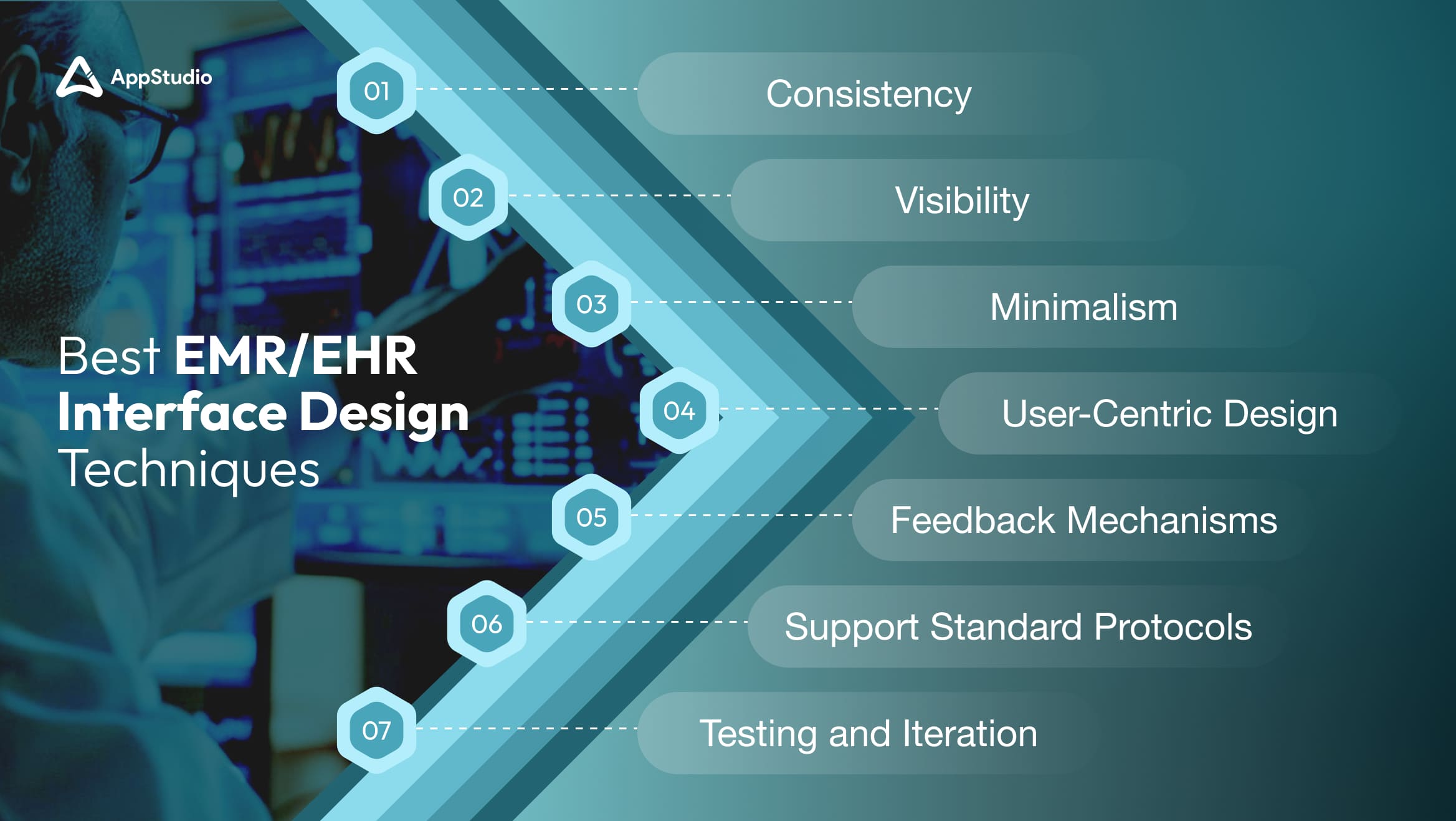
To enhance an EMR interface effectively, a series of best practices grounded in recent research and expert insights can be employed. Here are key techniques supportive of healthcare professionals’ needs:
1. Consistency
Consistency throughout the EMR interface is fundamental to usability. A uniform design logic, including similar color schemes, button placements, and labeling across sections, fosters intuitive navigation, reducing the time users need to familiarize themselves with different parts of the system.
Notably, adhering to data exchange standards such as HL7 (Health Level 7), a set of international guidelines for data sharing in healthcare, ensures smooth data exchanges between systems. Consistent design and compliance with standards improve the efficiency of healthcare workflows, allowing clinicians to retrieve and record patient data seamlessly.
2. Visibility
All essential information should be immediately visible and clearly presented to reduce the time spent searching for details. Displaying related data on a single screen—such as patient vitals, medications, and recent lab results—allows healthcare providers to make decisions without toggling between screens. This consolidated view is particularly valuable in critical care environments where quick access to comprehensive information can significantly impact patient outcomes.
3. Minimalism
A minimalist approach to EMR design eliminates non-essential steps, reducing distractions and enabling healthcare providers to perform tasks with fewer clicks. Simplified navigation that limits unnecessary options allows users to focus on high-priority tasks. For example, streamlining patient entry processes by auto-filling data fields wherever possible cuts down on repetitive inputs, helping healthcare teams save time and lowering the risk of errors.
4. User-Centric Design
Designing with specific user roles in mind—such as physicians, nurses, and administrative staff—tailors the interface to fit the needs of each group. For instance, an interface for a physician might prioritize access to patient history and diagnostic tools, while an interface for administrative staff could focus on scheduling and billing. This role-based customization minimizes cognitive load, as each user sees only the tools and information they need, streamlining their workflow.
5. Feedback Mechanisms
Real-time feedback provides users with immediate acknowledgment of their actions. For example, confirmation messages after saving patient records or error alerts if a field is left incomplete can reassure users and help them understand each process step. This feedback loop reduces uncertainty and improves confidence, allowing users to work more efficiently. Error alerts with clear instructions on resolving issues prevent frustration and guide users through corrective actions, enhancing overall usability.
6. Support Standard Protocols
Ensuring compatibility with standard protocols, such as FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources), enhances interoperability in healthcare, enabling smoother data exchanges between different systems and providers. This adherence to standards promotes a seamless flow of information, crucial for patient transfers between facilities. When an EMR is compatible with widely used protocols, healthcare professionals can access comprehensive patient histories and continue treatments without interruption, improving continuity of care.
7. Testing and Iteration
Regular usability testing with real users, including doctors, nurses, and administrative staff, is essential for gathering actionable feedback and refining the EMR interface. Testing allows developers to observe how users interact with the system, identify pain points, and understand which features need improvement. For instance, iterative testing might reveal that certain data fields are frequently misused or overlooked, prompting developers to adjust the layout for greater clarity. By continuously iterating based on feedback, the interface evolves to meet healthcare providers’ practical needs better
How Can AppStudio Help You Improve EMR/EHR Interface?
With expertise in EHR user experience design and a deep understanding of healthcare workflows, AppStudio is an industry-led Canada’s one of the most prominent mobile and app development agencies specializing in creating EMR/EHR interfaces that improve usability, efficiency, and user satisfaction. Here’s how AppStudio’s approach to EMR/EHR enhancement can benefit your healthcare organization:
1. Custom Development
AppStudio provides tailored solutions designed to meet each healthcare organization’s unique needs. By closely collaborating with clients, AppStudio ensures that the interface aligns with their environment’s specific workflows and operational requirements.
2. User Research and Testing
Understanding user needs is fundamental to AppStudio’s approach. AppStudio gains insights directly from the healthcare professionals who will use the system by conducting comprehensive user research and usability testing. Feedback from physicians, nurses, and administrative staff allows AppStudio to identify pain points and areas for improvement. This data-driven approach ensures the resulting interface is intuitive and aligns with real-world use cases.
3. Streamlined Workflows
To optimize the EMR interface, AppStudio conducts an in-depth analysis of existing workflows, identifying any inefficiencies or unnecessary steps. This approach allows AppStudio to simplify the interface, aligning it more closely with the day-to-day processes of healthcare providers.
4. Visual Clarity and Hierarchy
AppStudio focuses on creating visually intuitive interfaces, using clear hierarchies to guide users to essential information. By structuring data and functionality to align with how users naturally process information, AppStudio helps healthcare providers find what they need without confusion.
5. Continuous Improvement
AppStudio is committed to continuous improvement, recognizing that user needs and technology always evolve. Through iterative design, AppStudio collects and integrates ongoing user feedback, making adjustments as necessary to keep the interface aligned with current needs and technological advancements. This adaptive approach ensures the EMR/EHR interface remains relevant and user-friendly.
Related reading: Top 10 Mobile App Features in Healthcare
Wrapping Up!
Designing a simple, effective EHR user interface design is crucial for healthcare providers striving to balance patient care with digital administration. These interfaces reduce cognitive load and streamline workflows by incorporating clear navigation, consistent design elements, and user-centric customization. As a result, healthcare professionals can dedicate more time and attention to patient interactions, enhancing care quality and satisfaction on both sides.
With its user-centered approach, AppStudio specializes in creating EMR/EHR systems that adapt to evolving healthcare needs, ensuring usability, security, and continuous improvement. Through customized development, insightful research, and iterative design, AppStudio partners with healthcare organizations to develop solutions that align seamlessly with clinical workflows, reducing frustration and empowering providers to focus on what truly matters—improving patient outcomes. Schedule a FREE consultation with our expert today at AppStudio and change the course of how healthcare and administrative needs get revolutionized, one interface at a time.
Frequently Asked Questions
A user-friendly EMR interface allows healthcare providers to navigate the system more easily, reducing administrative time and enhancing the quality of patient care by focusing on essential functions.
Simplified interfaces reduce the cognitive load and frustration often associated with complex systems, helping alleviate stress and lowering burnout rates among healthcare professionals.
Customization allows users to personalize their workspace with frequently used tools and data, which improves workflow efficiency by minimizing the steps needed for routine tasks.
Through structured layouts and intuitive hierarchies, visual clarity helps users quickly locate necessary information, reducing time spent on navigation and minimizing the risk of errors.
Key security features include encrypted data storage, two-factor authentication, and automatic logouts to protect sensitive patient information and compliance with data privacy regulations.
Interoperability, supported by standards like FHIR, allows EMR systems to exchange data seamlessly with other healthcare applications, facilitating comprehensive patient records and continuity of care.
Minimalism reduces distractions, allowing healthcare providers to focus on critical tasks. This approach also streamlines workflows by minimizing unnecessary steps, ultimately improving efficiency.
Regular testing with real users and continuous iteration help refine the EMR interface to meet user needs better, enhancing usability and ensuring the system remains relevant as technology advances.