When it comes to streamlining patient information and care management, Electronic Health Record (EHR) software is indispensable. From improving accessibility to enhancing data security, the right EHR features can transform healthcare development practices. In 2023, the global EHR market was valued at approximately $29.68 billion, with projections indicating growth to $31.00 billion in 2024. This growth reflects a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.2% by 2032.
Morally, these statistics aren’t just some forecasted figures but a mirror image indicating that as healthcare providers prioritize efficiency and patient care management, the demand for thorough and error-free EHR software features is expected to rise exponentially–transforming how we see and use healthcare in the future, globally. Thus, this blog explores the top 10 EHR features with their benefits, adoption tips, and the latest trends in EHR technology to revolutionize your EHR workflow. Additionally, shedding light on how to make the best of these practices in your healthcare business to stay relevant in the coming times. Let’s begin.
What is EHR Software?
Electronic Health Record (EHR) software system is a digital tool that centralizes patient information, making it easy for healthcare providers to access medical history, treatment plans, and test results in one place. Unlike paper records, EHRs allow instant access to crucial data, improving care quality during consultations.
Besides storing medical records, EHR systems also handle the following:
- Appointment scheduling
- Medication management and billing
- Streamlining administrative tasks for providers to prioritize patient care and more.
EHR adoption has become essential for healthcare practitioners, especially with the rise of telehealth and remote consultations following COVID-19. EHRs enable real-time updates and support seamless coordination among healthcare teams, ensuring every provider has up-to-date information.
Essentials EHR Features and their Importance

EHR software is a cornerstone of modern healthcare, serving as a digital hub for patient data that supports efficient care management and improved patient outcomes. So, here are some EHR features list to follow and upgrade your healthcare service delivery.
This list of common features of the EHR will help you determine and underline the essentials regardless of your consumer base and clientele. Have a look:
1. Centralized Patient Data Access
EHRs consolidate all critical medical information in one place, making it easy for healthcare providers to access full patient histories, treatment plans, and test results in real time. This real-time access improves care quality by enabling informed decisions and timely interventions. A 2023 survey found that 70% of healthcare providers saw better patient outcomes with EHRs, underlining their impact in clinical settings.
2. Robust Data Security
With rising cyber threats and breaches becoming as common as possible, protecting sensitive health information is essential. EHR systems incorporate strong encryption and strict access controls, safeguarding patient data against unauthorized access and ensuring compliance with regulations like HIPAA. This security focus shields data and builds trust among patients, knowing their information is well-protected.
3. Enhanced Interoperability
EHRs enable smooth data exchange between different healthcare providers—specialists, labs, and pharmacies—which is crucial for coordinated care. This seamless information flow supports collaboration across healthcare teams, ensuring each provider has the most current data for every patient.
Related reading: What is EHR System and How to Build It? – Guide and Process
Tips for Adopting an EHR System Successfully

Integrating an EHR system into your practice may seem overwhelming, especially if it’s a first-time implementation or your team is transitioning from a different platform. However, a few key strategies can smooth the adoption process and benefit everyone involved. Here are essential tips for effective EHR adoption:
1. Evaluate Your Needs
Start by assessing your practice’s specific needs. What functions are most important for your workflow? For example, do you need robust appointment scheduling, customizable templates, or advanced data analytics?
Identifying the essential EHR features that align with your practice’s goals will help you select a system that genuinely supports your needs. In doing so, you avoid unnecessary features that may clutter the interface and cause confusion for users.
2. Engage Staff Early
Involving your staff from the beginning is crucial. When team members feel included in the decision-making process, they’re more likely to adopt the new system willingly. Start by gathering input from various departments to understand each team’s needs.
For instance, your administrative team may prioritize scheduling features, while clinicians may focus more on medical history access and charting capabilities. Early engagement also helps to address any initial concerns, fostering a smoother transition and reducing resistance.
3. Select User-Friendly Software
Choosing an intuitive, user-friendly EHR system reduces the learning curve and minimizes disruption to daily operations. Look for systems with straightforward interfaces, clear navigation, and minimal clicks for common tasks. Opting for a user-friendly EHR means your team can focus more on patient care and less on figuring out complex software. Some EHR providers also offer customizable layouts, allowing users to adapt the system to their preferences, improving satisfaction and productivity.
4. Conduct Regular Training Sessions
EHR implementation isn’t a one-time setup; it requires ongoing support and training. Schedule regular training sessions to keep your team up-to-date with system updates and best practices. Consistent training improves long-term efficiency as staff becomes more confident and skilled in using the software.
You can offer refreshers, bring in experts for specialized training, or set up peer-led sessions where more experienced staff members share tips. Investing time in training creates a knowledgeable team capable of maximizing the system’s capabilities.
10 EHR Features with Detailed Benefits

Some of the go-to and features an EHR must have are:
Trend 1: Patient Portal Access
Benefit: A patient portal gives patients direct access to their health records, test results, and treatment history. They can view their lab reports, check upcoming appointments, and even message their provider. This access fosters patient engagement by empowering them to take an active role in managing their health.
It also reduces the need for clinic calls for information requests, saving patients and healthcare staff time. In addition, enabling patients to monitor their progress strengthens trust and transparency between the healthcare provider and the patient.
Trend 2: Clinical Decision Support (CDS)
Benefit: Clinical Decision Support (CDS) is a powerful tool that helps healthcare providers make informed, timely clinical decisions. CDS systems analyze patient data to offer treatment suggestions, flag potential drug interactions, and alert providers to high-risk conditions. By incorporating real-time data into decision-making, CDS reduces human error and supports diagnostic accuracy.
For instance, if a patient is prescribed a medication that could interact with an existing one, the CDS will immediately alert the provider, helping prevent adverse effects and ensuring safer care.
Trend 3: E-Prescribing
Benefit: E-prescribing enables healthcare providers to send prescriptions to a pharmacy electronically. This feature reduces the errors associated with handwritten prescriptions and speeds up the medication dispensing, as prescriptions are sent instantly.
For patients, this means fewer trips back to the clinic due to prescription issues.
For providers, it reduces the chances of miscommunication and ensures a more streamlined medication management process, particularly beneficial for patients with chronic conditions requiring regular medication.
Related reading: What Is Interoperability in Healthcare? – A Complete Guide
Trend 4: Interoperability
Benefit: Interoperability enables seamless data exchange between different healthcare providers, systems, and facilities, ensuring that the most current patient information is available across various platforms. EHR system
For instance, a patient’s lab results can be shared instantly with a specialist or another healthcare provider, supporting more coordinated care. This capability is critical in emergencies or when multiple providers are involved in a patient’s treatment, as it helps prevent duplicate tests and speeds up care decisions.
Trend 5: Medical Billing Integration
Benefit: Medical billing integration automates billing and streamlines claims management. When billing is built into an EHR, data flows smoothly from patient records to billing, reducing manual input and minimizing errors. This feature helps speed up reimbursement cycles and reduces claim rejections, saving time and money.
For healthcare staff, it reduces repetitive administrative tasks, allowing more focus on patient care.
For patients, it simplifies payment processes, increasing their satisfaction.
Trend 6: Mobile Accessibility
Benefit: Mobile accessibility allows healthcare providers to access patient information, review records, and document care directly from a mobile device. This feature supports flexible, on-the-go healthcare delivery, essential in-home visits, telemedicine, or multi-location practices. It means faster patient response times, as providers can access and update records remotely. In addition, mobile access enhances communication between healthcare teams by allowing immediate updates on patient status and care plans.
Trend 7: Appointment Scheduling and Reminders
Benefit: EHR systems with integrated scheduling features streamline appointment booking by allowing patients to schedule or reschedule their visits online. Automated reminders are sent to patients, reducing no-shows and cancellations, improving clinic productivity and optimizing staff time management. Additionally, it provides patients a convenient way to manage appointments, reinforcing their engagement and satisfaction with the healthcare experience.
Trend 8: Data Analytics
Benefit: Data analytics within an EHR system processes large amounts of patient data to identify patterns, risk factors, and health trends. This information helps providers develop proactive care strategies, improving patient outcomes by anticipating and preventing health issues.
For example, analytics can identify high-risk patients for certain chronic diseases, allowing healthcare providers to tailor preventative care measures. This predictive approach supports overall population health management and contributes to better long-term health results.
Trend 9: Customizable Templates
Benefit: Customizable templates in EHRs help healthcare providers document patient encounters more efficiently by offering pre-filled forms that can be tailored to different visit types or conditions. This saves time during patient documentation and allows providers to record essential information without redundant steps. For example, pediatricians can use templates specific to childhood conditions, while orthopedic surgeons can have templates suited for musculoskeletal assessments. This customization increases workflow efficiency and ensures no critical information is missed.
Trend 10: Security and Compliance
Benefit: Built-in security features like encryption, two-factor authentication, and audit trails protect patient data from unauthorized access and cyber threats. Given the sensitive nature of medical records, compliance with data protection regulations is mandatory.
EHRs that incorporate strong security measures ensure compliance and build trust with patients by protecting their personal information. This security also mitigates risks for healthcare providers by reducing the likelihood of data breaches, which could lead to legal and financial repercussions.
How to Pick the Right EHR Software for Your Business?
Now that we have discussed the 10 features of an EHR system, here’s a step-by-step guide to help you make an informed decision regarding how to pick an EHR software for your healthcare business:
1. Determine Key Requirements
- Start by listing the must-have features that align with your practice’s daily operations and long-term goals.
- Consider which specific functionalities are paramount.
- Involve different departments in identifying needs to ensure the EHR caters to everyone’s workflow requirements.
Tip: Make a checklist of the features you want, and use it to compare EHR options.
2. Set a Budget
- EHR costs may vary immensely, from initial licensing fees to maintenance costs, so defining a budget upfront is essential.
- Cost considerations may include:
- One-time implementation fees or setup costs
- Subscription fees (if it’s a cloud-based EHR)
- Training and support fees
- Potential customization costs to tailor the EHR to your practice
- Strike a balance between your budget and feature needs, focusing on an EHR that offers the highest ROI for your practice.
Tip: Include hidden costs like data migration and periodic upgrades when setting the budget.
3. Trial and Testing
- Many EHR providers offer trial periods, allowing you to test the software in real-time.
- During the trial:
- Check the user interface for ease of use.
- Test the system’s speed and responsiveness with day-to-day tasks.
- Gather feedback from the team to assess whether the software meets their needs.
Tip: Conduct trial sessions across different departments to comprehensively view the system’s usability and fit.
Related reading: Top 10 Mobile App Features in Healthcare
4. Check Integration Capabilities
- An EHR that doesn’t integrate well with other software can create workflow issues and hinder efficiency.
- Look for integrations with:
- Billing and claims systems for seamless payment processing
- Laboratory and imaging systems for direct access to diagnostic results
- Patient portals to streamline patient engagement and communication
- Evaluate the EHR’s compatibility with your existing technology infrastructure, including hardware and software.
Tip: Confirm that the EHR is scalable and can integrate with future systems you may adopt as your practice grows.
5. Evaluate Vendor Support
- Support from the EHR vendor is essential for smooth setup, troubleshooting, and ongoing maintenance.
- Key aspects of vendor support include:
- Onboarding assistance for a seamless transition to the new system
- Training options to help your team fully understand and use the EHR
- Technical support availability (e.g., 24/7, online, or on-call)
- Regular updates and system upgrades to ensure security and functionality
- Read reviews or ask for references from existing clients to gauge the vendor’s responsiveness and reliability.
Tip: Ask the vendor for a demo or reference list to speak with other practices who use their system.
Overall, defining your specific requirements and integrating the processes involved in a checklist form can help you make an informed decision that enhances your operational efficiency and patient care quality.
EHR System and its Evolution Over the Years
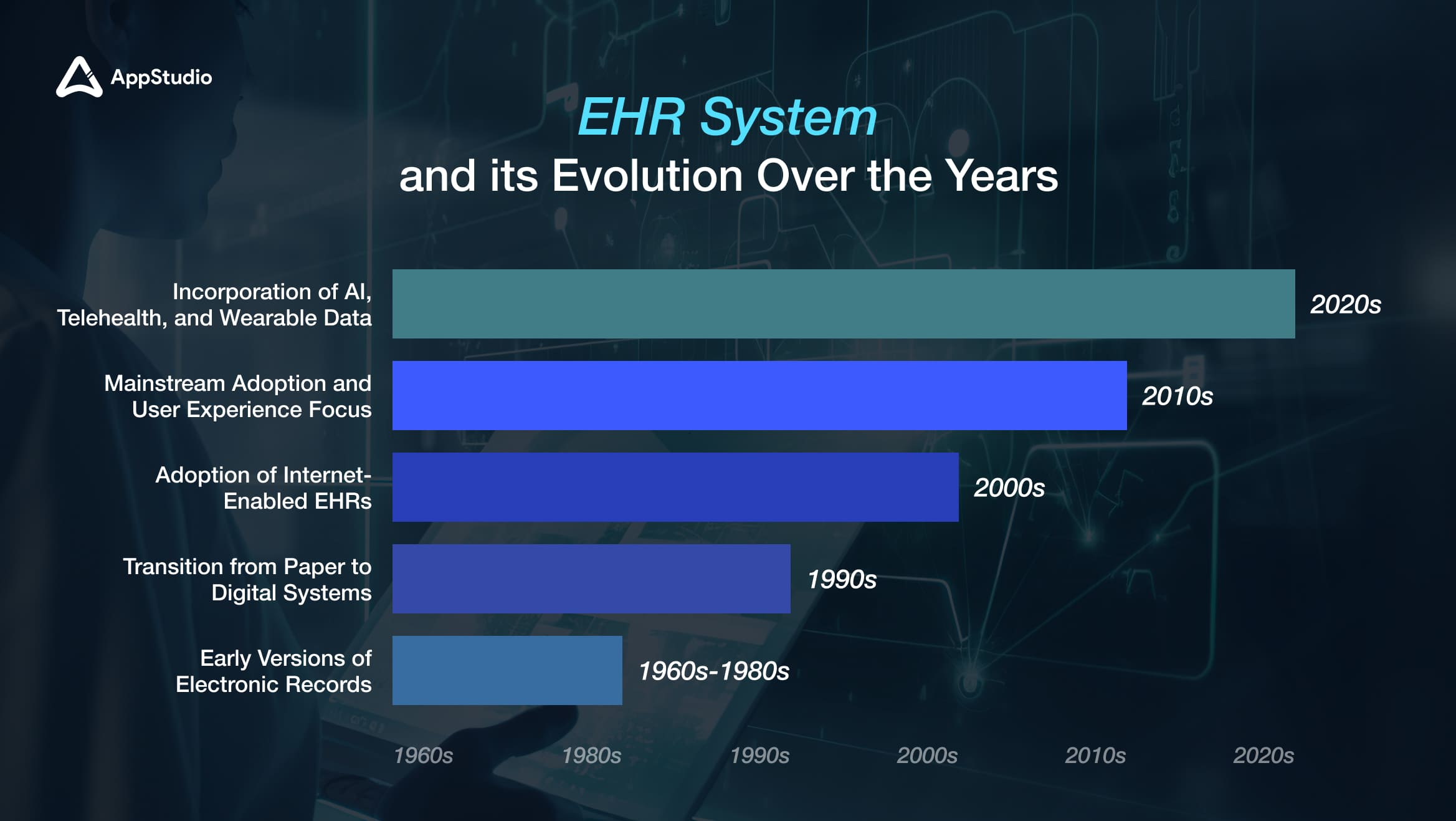
1. 1960s-1980s: Early Versions of Electronic Records
The first electronic health records emerged during the 1960s-1980s, primarily used in large hospitals for data storage. The Mayo Clinic was one of the pioneers in adopting electronic records, which were initially costly and limited in functionality. These early systems focused on storing patient data but lacked the ehr software features we associate with modern EHRs. The development of these systems laid the groundwork for future advancements in electronic health record technology.
2. 1990s: Transition from Paper to Digital Systems
The early 1990s marked a significant shift as healthcare providers transitioned from paper-based records to digital systems. This era introduced basic EHR features, such as electronic patient records, which improved data management and accessibility. The advent of the internet also played a crucial role in this transition, enabling more sophisticated digital solutions to emerge.
3. 2000s: Adoption of Internet-Enabled EHRs
In the 2000s, EHR systems became more advanced with the adoption of internet-enabled platforms that allowed for greater interoperability between different healthcare systems. This era saw an increase in the integration of various functionalities into EHR systems, such as appointment scheduling and billing. The introduction of government initiatives, like the Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health (HITECH) Act in 2009, further incentivized healthcare providers to adopt EHR systems by offering financial incentives for meeting meaningful use criteria.
4. 2010s: Mainstream Adoption and User Experience Focus
The 2010s marked a turning point as EHR systems became mainstream across healthcare practices. There was a strong emphasis on improving user experience and mobile accessibility during this decade. Healthcare providers began to prioritize intuitive interfaces that facilitated easier navigation and use by clinicians. This focus on user experience helped drive further adoption among smaller practices and enhanced overall satisfaction with EHR systems.
5. 2020s: Incorporation of AI, Telehealth, and Wearable Data
In the current decade, EHR systems have evolved to incorporate advanced technologies such as AI, telehealth compatibility, and data from wearable devices. These innovations make EHRs more intelligent and responsive to patient needs, allowing for real-time monitoring and proactive care management. The integration of telehealth features has become particularly important in light of the COVID-19 pandemic, enabling healthcare providers to deliver care remotely while maintaining access to vital patient information.
Related reading: Software Architecture for Healthcare Apps
Wrapping Up!
In today’s healthcare environment, effective EHR software is more than just a digital record system; it’s a transformative tool that simplifies workflows, enhances patient outcomes, and strengthens data security. By centralizing patient information and automating repetitive tasks, owning the essential features of an EHR system enable healthcare professionals to focus more on patient care rather than administrative burdens, essential for delivering high-quality service.Choosing an EHR system features must empower providers to streamline operations, reduce errors, and foster a more collaborative approach to care. By investing in the right EHR software, healthcare providers can adapt to an increasingly digital and connected world, achieving greater efficiency and delivering superior care. A thoughtfully selected EHR system, supported by strong digital partnership like AppStudio’s, becomes a long-term asset, positioning healthcare practices for growth and success in a continuously evolving landscape. Schedule a Free Consultation and revolutionize your ehr features unlike ever before.
Frequently Asked Questions
Key features of EHR include patient portals, interoperability, e-prescribing, data security, and clinical decision support. Each function is vital in enhancing patient engagement, improving coordination among healthcare providers, and safeguarding sensitive health data.
Interoperability allows different healthcare systems to communicate seamlessly, facilitating coordinated patient care across various providers. This capability helps reduce redundant testing and ensures all care providers can access the latest patient information.
EHR systems enhance patient care by providing quick and secure access to complete health records, supporting timely and accurate diagnoses. Additionally, EHRs reduce medical errors and empower providers to make data-driven decisions that can improve overall patient outcomes.
E-prescribing enables healthcare providers to send prescriptions electronically to pharmacies, eliminating the need for handwritten scripts. This process reduces errors, speeds up medication fulfillment, and enhances patient convenience by minimizing prescription delays.
Data analytics within EHR systems help providers track health trends, anticipate patient needs, and tailor preventative care strategies. By analyzing patient data, healthcare providers can make informed decisions and improve health outcomes across their patient population.