The healthcare industry is undergoing a major transformation as the future of IoT in healthcare emerges as a powerful force by 2025. Connected devices like wearables and remote monitoring tools enable the real-time tracking of vital signs, helping doctors make timely decisions and deliver care. Statista predicts nearly 200 million healthcare IoT devices by 2025, highlighting their growing importance in improving patient outcomes and streamlining healthcare operations.
The future of IoT in healthcare looks even brighter with the integration of 5G technology, which will enhance communication between devices and expand access to telemedicine and remote care. This market is expected to grow, with projections estimating it could reach $822.54 billion by 2032, transforming the industry. In this blog, you’ll discover how IoT is driving innovations that go beyond traditional healthcare and why IoT in healthcare is becoming indispensable, transforming care delivery for both providers and patients.
What is IoT and How is it Changing Healthcare Dynamics?
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a network of smart devices that communicate with each other to share and process data in real-time. In healthcare, it connects tools like wearable health monitors, smart medication dispensers, and diagnostic devices to improve how care is delivered. This seamless connection allows healthcare providers to make faster, more informed decisions, enhancing both patient care and operational efficiency.
Building on earlier insights, the global IoT in the healthcare market is on a sharp rise. By 2032, it is expected to reach $822.54 billion, fueled by a compound annual growth rate of 21.3%. This expansion highlights the demand for connected medical devices and automated remote patient care underlining the multiple advantages of IoT in healthcare.
The dynamics of healthcare are shifting quickly. One of the key drivers of this impact of IoT in healthcare is the rise in adoption of wearable health devices. These devices enable real-time tracking of vital signs, helping healthcare providers with actionable insights. This trend is expected to fuel the growth of the IoT healthcare market, which is projected to reach $184.49 billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 19.5% from 2024.
In addition, remote patient monitoring—a cornerstone of IoT applications in healthcare—is seeing a high demand. The global remote patient monitoring market is estimated to grow from $5.2 billion in 2023 to $9.9 billion by 2030, reflecting a CAGR of 18.6%. Let’s also explore why IoT in healthcare and the benefits of iot in healthcare is transforming the industry and how it’s becoming a game-changer for both providers and patients.
Related reading: Top 10 Mobile App Features in Healthcare
Why Use IoT in Healthcare?
IoT in healthcare is revolutionizing how care is delivered, bringing significant improvements for both patients and providers. One of the leading reasons to use IoT in healthcare is remote patient monitoring, which enables real-time tracking of vital signs. This technology has reduced hospital readmissions by up to 50% for patients with chronic conditions, ensuring better health outcomes while easing the strain on healthcare facilities.
IoT devices also gather detailed patient data, empowering healthcare professionals to create personalized treatment plans tailored to individual needs. This level of customization leads to more effective care and fosters stronger patient engagement. By improving access to real-time information and enabling proactive interventions, IoT benefits in healthcare go beyond operational efficiency—they create a more connected, responsive, and patient-centered system. Moreover, IoT improves operational efficiency by optimizing workflows and lowering administrative costs, enabling healthcare providers to dedicate more time to patient care than paperwork.
IoT Applications in Modern Healthcare

The impact of IoT in healthcare is undeniable, with smart devices revolutionizing how care is delivered and managed. IoT technology in healthcare bridges the gap between patients and providers, creating a more connected and responsive system. Below, we explore the essentials of IoT in healthcare and how these applications are transforming patient care and operational workflows.
1. Remote Patient Monitoring
IoT devices continuously track patients’ vital signs, such as heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen levels. This enables healthcare providers to detect abnormalities early, intervene promptly, and improve chronic disease management, significantly reducing hospital readmissions.
2. Wearable Health Monitors
These devices gather data on key health metrics like activity levels, sleep patterns, and more. By analyzing this information, healthcare professionals can make tailored recommendations for lifestyle changes or treatment plans, creating a more personalized approach to care. The wearable biometric monitor market is expected to reach $25.03 billion by 2034, with a CAGR of 8.9%.
3. Telehealth Solutions
IoT technology in healthcare devices facilitate seamless remote consultations by transmitting real-time health data during virtual appointments. This enables healthcare providers to make precise diagnoses and develop treatment plans without needing in-person visits, expanding access to care for patients in remote or underserved areas.
The global telehealth market is projected to grow significantly, reaching an estimated $851 billion by 2032. The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated its adoption, showcasing the convenience and effectiveness of remote healthcare. As telehealth continues to evolve, it promises to make quality care more accessible and efficient for patients worldwide. This move makes the benefits of using IoT in healthcare more imperative and needful than ever.
4. Connected Imaging Devices
IoT-powered imaging tools allow diagnostic images to be shared in real-time with specialists, improving collaboration across healthcare teams. This leads to faster diagnoses, better-informed decisions, and enhanced patient outcomes.
Related reading: What Is Interoperability in Healthcare? – A Complete Guide
Why does security matter for IoT in healthcare?
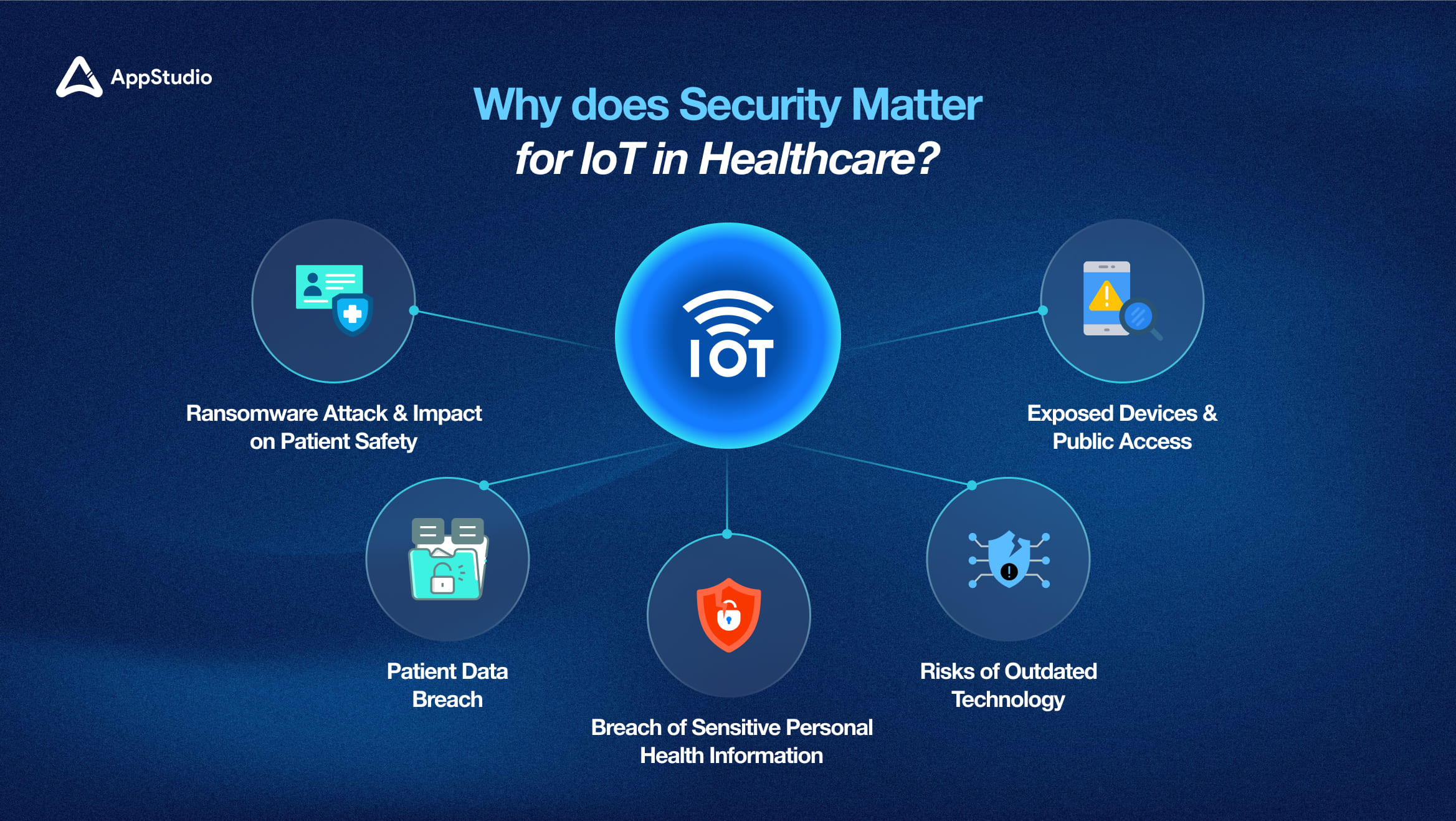
As IoT becomes integral to modern healthcare, it brings both opportunities and risks. These real-world breaches underline the urgency for robust security measures in safeguarding patient lives and data and how devastating the consequences can be.
1. Exposed Devices and Public Access
In 2024, more than 14,004 unique IP addresses were found exposing healthcare devices and systems to the public internet. This widespread exposure opens countless entry points for potential cyberattacks. A notable example involves the exploitation of open Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine (DICOM) ports. These vulnerabilities have been leveraged in data extortion schemes, where attackers gain unauthorized access to sensitive medical imaging data
2. Breach of Sensitive Personal Health Information
Cybercriminals often target PHI because of its high value, as it can be used for identity theft or sold on the black market. The consequences of a breach go beyond financial losses; they can erode patient trust and disrupt care. A striking example occurred in 2024 when Kaiser Permanente inadvertently exposed the personal information of up to 13.4 million Americans. Data was mistakenly shared with third parties, including search engines like Google and Bing.
3. Risks of Outdated Technology
With the rapid expansion of IoT in healthcare, many devices are running on outdated technology, creating significant security risks. Devices with old firmware or weak encryption are prime targets for cybercriminals, providing them with easy entry points to exploit sensitive systems.
A recent example is the 2024 cyberattack on INTEGRIS Health, where hackers accessed the private health information of nearly 2.4 million individuals, including Social Security numbers.
4. Ransomware Attack & Impact on Patient Safety
Cybersecurity breaches in healthcare don’t just affect data—they can put lives at risk. When systems are compromised, care delivery is disrupted, leading to delays that directly impact patient safety. Ransomware attacks, for instance, have been linked to higher patient mortality rates and longer hospital stays, as critical procedures are postponed.
A startling statistic reveals that 28% of healthcare organizations reported procedural delays due to ransomware, resulting in poor patient outcomes.
5. Patient data breach
In 2023, Geisinger, a Pennsylvania-based health system, faced a significant data breach impacting over 1.2 million patients. The breach was linked to Nuance Communications, an external vendor, and was caused by a former Nuance employee who accessed patient information just two days after their termination. It shows how important it is to limit access to patient data based on job roles and terminate access immediately when an employee leaves, whether internal or with a vendor.
Key Challenges in Managing IoT Security in Healthcare 2025
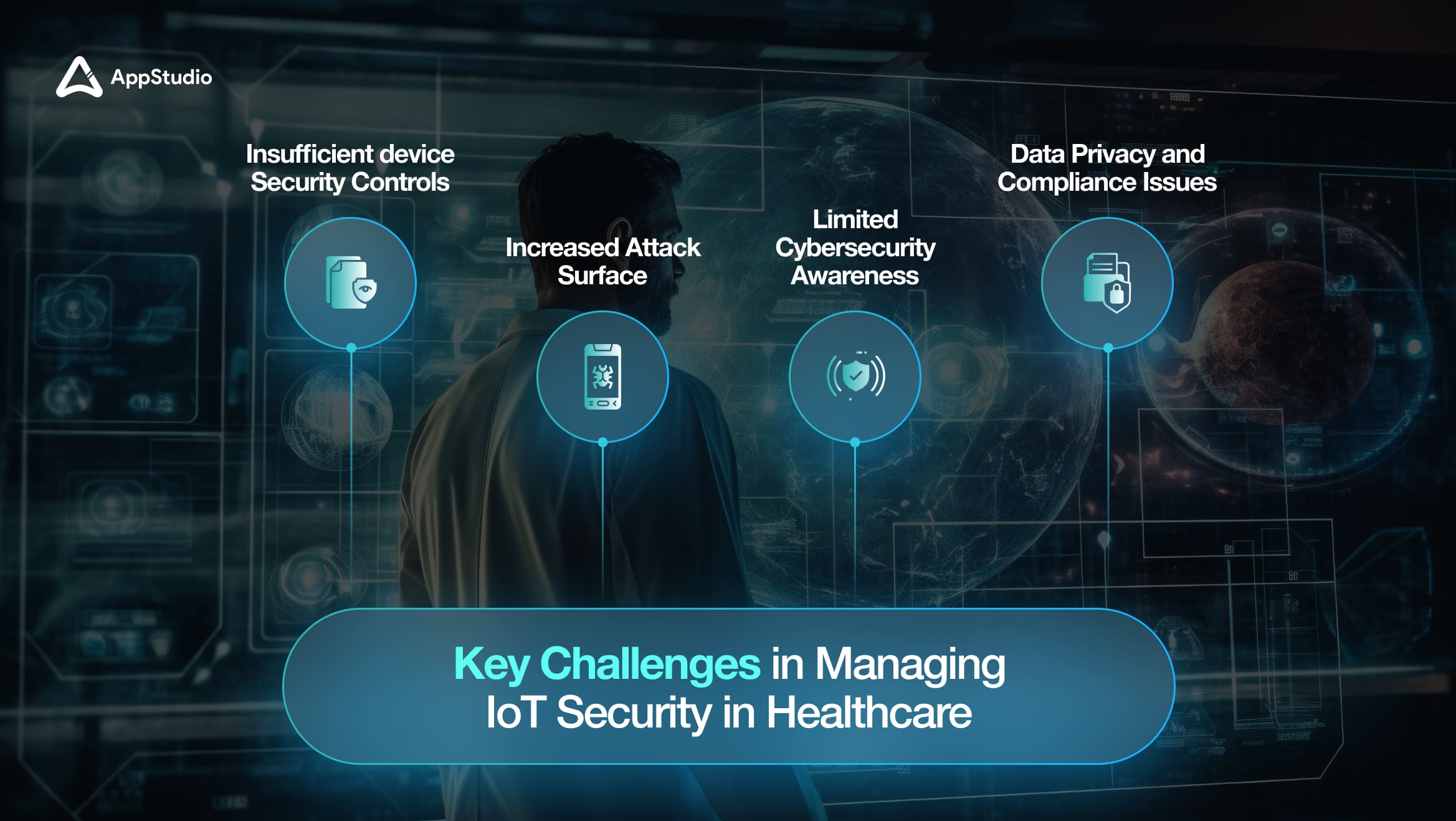
The rise of IoT in healthcare is transforming patient care and operational efficiency, offering unprecedented benefits. However, these advancements come with significant security challenges that healthcare organizations must address to protect sensitive data and ensure system reliability. Understanding the importance of IoT in healthcare and the challenges of IoT in healthcare involves recognizing and tackling these critical vulnerabilities as we approach 2025.
1. Insufficient device Security Controls
Many IoT devices, like infusion pumps and wearable monitors, lack strong security measures, making them vulnerable to cyberattacks. Often, these devices can’t support regular updates or advanced security features, leaving critical medical equipment exposed. Regulatory restrictions can further complicate the implementation of necessary safeguards.
Solution: To overcome such IoT challenges in healthcare, providers should adopt security-by-design principles when deploying devices. This includes ensuring built-in security features, enabling regular firmware updates, and using strong encryption protocols. By prioritizing proactive security measures, organizations can reduce risks and protect both patient data and safety.
2. Increased Attack Surface
The growing number of IoT devices in healthcare has led to networks with thousands of connected endpoints, each acting as a potential entry point for cybercriminals. This expanded attack surface makes healthcare systems more vulnerable to threats if security measures are not robust and comprehensive.
Solution: Healthcare organizations can mitigate these risks by implementing network segmentation, which isolates sensitive areas of the network to limit access and contain potential breaches. Adding continuous monitoring and advanced threat detection systems ensures that suspicious activities are identified and addressed promptly, reducing the chances of widespread damage.
3. Data Privacy and Compliance Issues
Personal health information (PHI) is highly sensitive, making healthcare a prime target for cybercriminals. Breaches not only expose confidential data but also have serious consequences for both patients and organizations.
Solution: Healthcare organizations can address these challenges by implementing robust compliance programs, including regular audits to ensure IoT devices meet regulatory standards. Advanced encryption should be used to protect data both at rest and in transit, preventing unauthorized access while maintaining legal compliance.
4. Limited Cybersecurity Awareness
Healthcare providers often prioritize patient care over cybersecurity investments, leaving IoT vulnerabilities exposed. This lack of awareness makes the industry a frequent target for ransomware and denial-of-service attacks, putting both data and operations at risk.
Solution: Regular cybersecurity training for all staff can bridge this gap by increasing awareness of potential threats and best practices for protecting IoT devices. Building a culture of cybersecurity empowers employees to identify vulnerabilities, respond to incidents effectively, and create a more secure healthcare environment.
Related reading: How is IoMT Revolutionizing the Healthcare Industry?
Strategies for Securing IoT Devices in Healthcare
With this growing reliance on IoT in healthcare, comes the critical challenge of ensuring their security. Cyberattacks targeting healthcare systems not only compromise sensitive patient data but can also disrupt life-saving medical operations. To fully realize the importance of IoT in healthcare while safeguarding its use, healthcare organizations must adopt effective strategies to mitigate risks and protect their IoT ecosystems.
The future of IoT in healthcare lies in its ability to improve patient outcomes and operational efficiency. Still, these benefits can only be realized if robust security measures are in place.
Strategy 1: Strong Authentication Mechanisms
Simple passwords are no longer enough to protect IoT devices. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) provides an additional layer of security by ensuring that only authorized users can access devices. Combining strong, unique passwords with biometric verification helps prevent unauthorized access to sensitive systems and information.
Why it is helpful: Strong authentication reduces the risk of unauthorized access to sensitive systems and patient information. With over 53% of IoT medical devices facing serious security threats, implementing MFA ensures healthcare organizations can better protect their data & safeguard patient privacy.
Strategy 2: Regular Software and Firmware Updates
Outdated software is a common target for cyberattacks. Regularly updating device software and firmware helps close security gaps by addressing known vulnerabilities. Automating updates wherever possible ensures devices remain protected against emerging threats without manual intervention.
Why it is helpful: Keeping IoT devices up to date minimizes the chance of exploitation from security gaps. With 12% of healthcare attacks originating from IoT devices, regular updates are essential to maintaining the safety and functionality of medical equipment, ultimately protecting patient health and ensuring uninterrupted care.
Strategy 3: Data Encryption
Encrypting data at rest and in transit is crucial for protecting sensitive health information. By using industry-standard encryption protocols, healthcare organizations ensure that even if a device is compromised, the data remains unreadable to unauthorized users, preserving confidentiality.
Why it is helpful: Encryption is a critical defense against data breaches, securing patient information even if intercepted by attackers. It also ensures compliance with strict regulations like HIPAA, which require robust data protection measures.
How Will 5G Impact IoT in Healthcare in 2025?
The healthcare landscape is changing rapidly, and at the heart of this transformation is 5G technology. Once limited by slower networks and high latency, healthcare providers are now leveraging 5G to unlock unprecedented opportunities for better care. In 2024, the global 5G healthcare market was valued at $2.72 billion, but it’s expected to soar to $22.60 billion by 2031, growing at an impressive CAGR of 35.3%.
Consider connectivity: under 4G networks, only 2,000 devices could connect per square kilometer, limiting the scalability of IoT in healthcare. With 5G, up to 1 million devices can operate within the same space, supporting advanced applications like real-time patient monitoring and interconnected smart devices. This isn’t just an upgrade in speed; it’s a shift that’s making healthcare smarter, more connected, and more responsive to patient needs. Below are a few examples of what all 5G can help the healthcare industry achieve.
Increased Device Connectivity
5G’s capacity to handle many connected devices simultaneously will support smart hospitals. These devices will work together seamlessly, from wearables to diagnostic tools, enabling optimized care and efficient resource management. It’s estimated that over 2 million 5G-enabled IoT connections will be used in healthcare by 2030, highlighting the scalability and potential of this technology.
Support for Advanced Medical Technologies
IoT trends in healthcare, such as robotic surgery and remote-assisted procedures, will thrive with 5G’s speed and reliability. Surgeons can operate robotic systems from afar, bridging gaps in specialized medical care. This precision-driven approach will help address healthcare disparities, ensuring patients in underserved regions receive top-tier treatments.
Improved Telemedicine Services
5G’s high-speed connectivity will elevate telemedicine experiences, offering smooth, high-quality video consultations without interruptions. This will make IoT benefits in healthcare more accessible, especially for patients in remote areas. With more patients open to digital health consultations, 5G will play a vital role in meeting this demand while enhancing convenience for both providers and patients.
Related reading: Software Architecture for Healthcare Apps
Wrapping Up!
At AppStudio, we understand the transformative potential of IoT benefits in healthcare and how technologies and tools can revolutionize care delivery. Our team at AppStudio specializes in designing secure, scalable, and innovative IoT solutions tailored to healthcare providers’ unique needs. Whether real-time patient monitoring, advanced telemedicine platforms, or smart hospital systems, we ensure your technology works seamlessly to improve patient outcomes and streamline operations.
Our expertise spans from designing innovative IoT applications to implementing secure and efficient systems, and can work together to create a healthcare ecosystem that’s smarter, more seamless, and patient-focused.
Whether you’re aiming to integrate more capabilities or enhance your existing IoT framework, AppStudio is your trusted partner. Reach out for a free consultation today and take the first step toward a more connected and efficient healthcare system.
Frequently Asked Questions
By 2025, IoT in healthcare will enable real-time monitoring of vital signs, facilitate personalized treatment plans using data-driven insights, and enhance telemedicine services. These advancements promise more timely interventions, reduced hospital visits, and improved health outcomes.
IoT in healthcare helps providers improve operational efficiency, streamline patient management, and reduce costs related to unnecessary hospital visits. Real-time data from connected devices also enables timely interventions, enhancing the quality of care delivered.
Yes, many IoT devices offer patients access to their health data via mobile apps or web portals. This empowers individuals to monitor and manage their health actively, promoting better engagement and wellness outcomes.
Devices like wearable monitors track vital signs, remote monitoring systems provide real-time health updates, smart dispensers manage medication schedules, and connected imaging tools facilitate accurate and timely diagnosis, all contributing to better patient care.
AppStudio specializes in creating tailored IoT applications designed to meet the specific needs of healthcare providers. Our expertise ensures secure, scalable solutions that integrate smoothly with existing systems, enhancing patient care and operational efficiency.







