The use of mobile apps in healthcare has skyrocketed in recent years; according to a report by Statista, the global digital health market is expected to reach $660 billion by 2025. This tremendous growth is fueled by the increasing need for convenient, accessible, and efficient healthcare services, making healthcare mobile apps a key player in modern medical practices. This blog will explore the importance of healthcare in mobile apps, must-have features for healthcare professionals (HCPs) and patients, and critical considerations for developing a successful mHealth app.
Importance of Healthcare in Mobile Apps
In today’s fast-paced world, healthcare mobile apps serve as vital tools for both patients and healthcare professionals. They streamline processes, improve patient outcomes, and make healthcare services more accessible to a broader audience. For example, healthcare mobile apps features like telemedicine allow patients to connect with doctors from the comfort of their homes, while HCPs benefit from features like real-time data monitoring and electronic health records (EHRs).
Let’s break down the importance of these apps:
1. Improved Accessibility
Improved accessibility through healthcare mobile apps means patients can access medical advice, prescriptions, and consultations without being physically present at a clinic or hospital. This includes features like telemedicine, e-prescriptions, and instant messaging with healthcare providers.
Why: Accessibility is crucial, especially for patients living in remote areas or those with mobility issues. Instead of traveling long distances or waiting in clinics, they can consult with doctors from the comfort of their homes. It also ensures that patients can access medical care at any time, not just during traditional office hours, making healthcare more patient-centric.
Example: Doctor On Demand, Teladoc, MyChart
2. Real-Time Monitoring
Real-time monitoring involves continuously tracking patient health data, such as heart rate, blood pressure, glucose levels, or sleep patterns, using wearable devices like smartwatches or fitness trackers. This data is synced with healthcare mobile apps, where healthcare providers (HCPs) can monitor these vitals in real time.
Why: Monitoring a patient’s vital stats in real-time allows HCPs to make timely decisions. For patients with chronic conditions, such as diabetes or heart disease, real-time monitoring can prevent complications by detecting anomalies early.
Example: Apple Health, Google Fit, Fitbit
3. Reduced Costs
Mobile healthcare apps can significantly lower healthcare costs by reducing the number of unnecessary in-person visits and streamlining processes such as prescription refills and follow-up consultations.
Why: Healthcare costs are a significant concern for both patients and providers. By minimizing unnecessary clinic visits, apps save time, reduce patient travel expenses, and lower operational costs for healthcare providers.
Example: Amwell, Talkspace, First Derm
Related reading: Software Architecture for Healthcare Apps
Healthcare App Features for HCPs & Patients
Developing a health-related mobile app that includes the right set of healthcare app features is essential for creating a useful tool that benefits both HCPs and patients.More than 85% of healthcare organizations are now investing in mobile apps, IT tools and digital budgets to enhance patient care, according to a report by Guidehouse Analysis. Here’s a list of some impactful features that can be incorporated to meet the needs of HCPs and patients alike:
For Healthcare Professionals (HCPs)
1. Electronic Health Records (EHRs)
EHRs allow healthcare providers to access a centralized, digital repository of patient medical histories, diagnoses, lab results, and treatment plans. This streamlined access improves diagnostic accuracy, treatment planning, and overall efficiency by eliminating the need for manual record-keeping.
For example, doctors can review a patient’s history, including previous treatments or surgeries, in seconds, ensuring no critical details are missed. It also enables collaboration among healthcare providers, as multiple specialists can access the same patient file.
2. Real-Time Alerts
Real-time alerts notify HCPs of any significant changes in a patient’s vital signs, such as abnormal heart rates, blood pressure fluctuations, or glucose levels. Thus, immediate notification is crucial for managing chronic conditions or emergencies, allowing healthcare professionals to act quickly and prevent complications.
For example, a doctor treating a heart patient can receive an alert if the patient’s heart rate spikes beyond a safe threshold, enabling rapid intervention even if the patient is not in a hospital setting.
3. Telemedicine Integration
Telemedicine allows HCPs to conduct remote consultations via video or voice calls, eliminating the need for in-person visits in many cases. This feature increases accessibility for patients, reduces appointment wait times, and expands the reach of healthcare providers, especially in remote areas. Telemedicine has seen a 300% increase in usage since 2020, according to McKinsey & Company.
For example, doctors can diagnose and treat minor ailments like cold symptoms or monitor post-surgical recovery through telemedicine without patients needing to visit the clinic, saving time and resources for both parties.
4. Data Analytics
Data analytics tools use AI to collect and analyze patient data, providing insights into trends, treatment effectiveness, and patient outcomes. These analytics help healthcare providers make informed, data-driven decisions and adjust treatment plans as needed, improving patient care and operational efficiency.
For example, a healthcare app might analyze data from hundreds of diabetes patients and provide insights on which treatments lead to the most stable blood sugar levels, helping doctors optimize care for future patients.
Related reading: Healthcare Mobile App Development: Blueprint For Startups & SMEs
For Patients
1. Appointment Scheduling
Patients can book, modify, or cancel appointments directly through the app, without the need to call or visit the clinic. This improves patient convenience, reduces missed appointments, and streamlines the scheduling process for healthcare providers.
For example, patients with busy schedules can easily manage appointments at any time by receiving automatic reminders, which, according to NCBI, can increase patient walk-ins and reduce no-shows by 5 to 7.4%.
2. Medication Reminders
The app alerts patients when it’s time to take their prescribed medications. For patients with chronic conditions or multiple prescriptions, forgetting to take medications can be harmful. Medication reminders help ensure adherence, improving treatment outcomes.
For instance, an app can remind a patient to take their blood pressure medication at the same time each day, helping them stay consistent with their treatment plan.
3. Health Monitoring
Patients can use the app to track their health metrics, such as blood pressure, glucose levels, or physical activity, which can be synced with wearable devices. Regular health monitoring empowers patients to take control of their well-being and share crucial data with their healthcare providers, enabling better ongoing care.
For instance, a diabetic patient can monitor their blood sugar levels daily, and the data is automatically sent to their doctor for regular review, ensuring any irregularities are addressed quickly.
4. Access to Medical Records
Patients can view their lab results, medical histories, and treatment plans through the app, improving transparency and engagement in their care. Access to their medical records allows patients to stay informed and make decisions regarding their health, increasing patient empowerment.
For example, after a medical test, patients can view their lab results instantly through the app, instead of waiting for a call from the doctor’s office and having it picked.
Therefore, by integrating these essential and go-to healthcare app features for doctors and patients alike, such applications can provide efficient healthcare delivery at their fingertips.
Related reading: How is IoMT Revolutionizing the Healthcare Industry?
10 Trending Features for Healthcare Apps
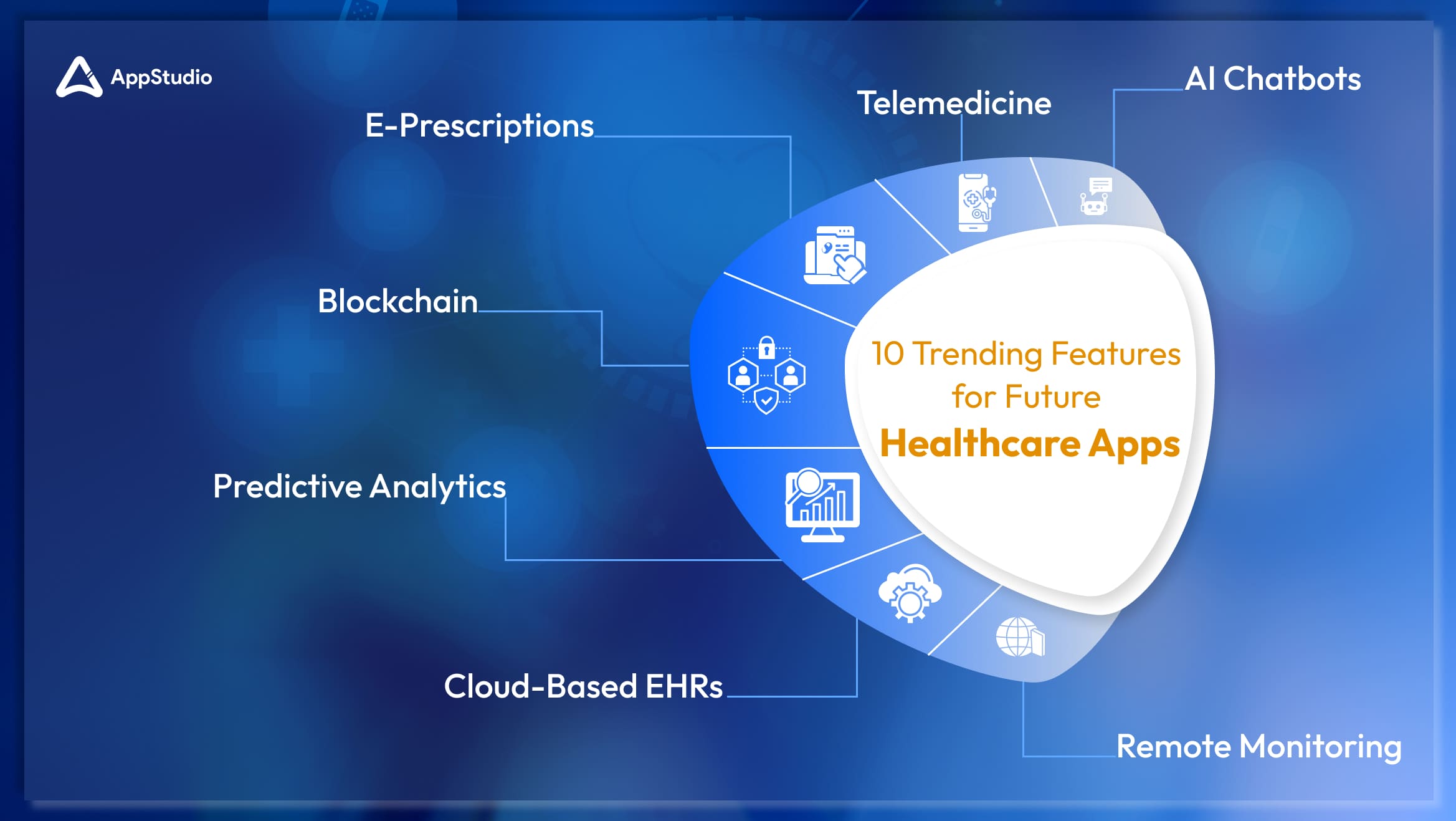
The healthcare industry has undergone significant technological advancements, and mobile apps are at the forefront of this evolution. These healthcare app features are gaining and are likely to stay and become even more prominent with years passing by, reflecting both current demands and future trends. Let’s explore how each feature is relevant today, its potential future benefits, and how it can transform the healthcare and tech industries.
1. AI Chatbots
AI-powered chatbots have quickly become indispensable in the healthcare sector. These virtual assistants provide 24/7 support for patients by answering common health queries, triaging symptoms, and directing users to the appropriate level of care. In an era where healthcare systems are often seen as underwhelmed due to a lack of technological investments, AI chatbots help reduce this burden on a budget, especially for medical staff, by handling routine inquiries and freeing up time for doctors to focus on cases, more critical.
And as times are a changin’, so are the advancements with AI. These chatbots are expected to evolve, offering increasingly personalized recommendations based on patient data and even providing preliminary diagnoses. This progression makes AI chatbots an exciting frontier in patient care, offering more tailored health support in the near future.
2. Telemedicine
Just as AI chatbots are evolving, similarly, telemedicine has experienced an exponential rise, particularly after the COVID-19 pandemic. Telemedicine enables patients to consult healthcare professionals via video or audio calls, eliminating the need for in-person visits. This not only reduces the risk of exposure to contagious diseases in waiting rooms but also allows healthcare providers to extend their services to remote areas where access to physical clinics is limited.
With the expansion of 5G networks, telemedicine will become even more seamless, allowing for high-quality video consultations and improving healthcare accessibility even in rural areas. Platforms like Teladoc have already paved the way for telemedicine, and their growing user experience base indicates that this feature will likely remain a cornerstone of digital healthcare for years to come.
3. E-Prescriptions
In tandem with telemedicine, e-prescriptions are making paper-based systems obsolete. Doctors can now send prescriptions directly to pharmacies digitally, eliminating the risks associated with illegible handwriting or communication errors. This streamlines the prescription process, saving time for both patients and pharmacists. Patients no longer need to carry prescriptions physically, and pharmacists can prepare medications in advance, reducing wait times and improving efficiency. Additionally, e-prescriptions offer enhanced security, helping to prevent prescription fraud and ensuring that medications are dispensed accurately.
Looking ahead, the integration of AI with e-prescriptions holds immense potential. In the future, AI can analyze a patient’s medical history, current medications, and genetic predispositions to suggest the most appropriate treatments. This could lead to more personalized prescriptions, reducing the risk of adverse drug interactions and improving overall treatment outcomes. By continuously learning from patient data and clinical research, AI-powered e-prescriptions could also assist healthcare providers in making more informed, evidence-based decisions, further optimizing patient care and enhancing safety.
4. Remote Monitoring Anywhere, Anytime!
Another game-changing feature is remote monitoring, which enables healthcare providers to track patients’ vital signs, such as heart rate, glucose levels, and oxygen saturation, in real-time through connected devices. This feature is particularly valuable for patients with chronic conditions like diabetes and hypertension, as it allows for continuous monitoring and early detection of potential complications. For kids, caretakers away from their parents and guardians can easily monitor their well-being and track health status using remote monitoring as a feature. Remote monitoring also drastically reduces the need for frequent hospital visits, offering significant benefits in areas with limited healthcare resources.
As IoT development technology advances, remote monitoring tools will become more sophisticated, providing even more comprehensive data collection and deeper insights into patient health. For instance, Medtronic’s Guardian Connect already allows diabetic patients to monitor glucose levels in real time, preventing emergencies and improving overall care.
5. Blockchain for Data Security
With the rise of digital healthcare, data security has become a paramount concern, and blockchain technology offers a solution. Blockchain provides a decentralized method of storing and securing sensitive patient data, ensuring data integrity and preventing unauthorized access. As cyberattacks on healthcare systems increase, blockchain technology adds an extra layer of protection, making it incredibly difficult for hackers to alter medical records.
Looking ahead, blockchain development has the potential to create a unified global healthcare data system, allowing secure and seamless data sharing across healthcare providers without compromising privacy. Medicalchain is one example of a platform leveraging blockchain to protect patient information, representing the future of secure, transparent healthcare data management.
Related reading: Top 8 Virtual Healthcare Apps Revolutionizing the Healthcare Sector
6. Cloud-Based EHRs for Easy Accessibility
Cloud-based Electronic Health Records (EHRs) further streamline healthcare by allowing healthcare providers to access patient data from anywhere. Cloud storage eliminates the need for bulky physical files, making patient data accessible in real time and enabling quicker and more accurate diagnoses. Moreover, cloud-based EHRs foster better collaboration between healthcare professionals, as patient data can be shared seamlessly across different locations.
As cloud development technology continues to evolve, EHRs will enhance global interoperability between healthcare providers, reducing redundant tests and treatments. Cerner, a leader in cloud-based EHRs, exemplifies how this technology improves patient care by providing up-to-date medical information on demand.
7. Predictive Analytics for Early Disease Detection
With the growing amount of health data being collected, predictive analytics is emerging as a critical feature. Powered by AI and ML, predictive analytics uses patient data to anticipate potential health issues before they turn into serious conditions. By analyzing factors such as genetic predispositions, lifestyle choices, and past medical history, predictive models can identify early signs of diseases, allowing for proactive intervention.
Healthcare is often reactive, as seen today—patients seek treatment after symptoms appear. But predictive analytics transforms this model and pattern of checkups by enabling early diagnosis, which can dramatically improve outcomes for conditions like heart disease, cancer, and blood sugar. This shift from reactive to preventive healthcare will not only improve patient quality of life but also reduce the long-term costs associated with treating chronic diseases. A report by Frost & Sullivan suggests that using AI, predictive analytics, and cognitive computing in healthcare may generate savings of over $150 billion or more by 2025 for the healthcare industry. Thus, in the future, apps will combine real-time health data from wearables with predictive algorithms to provide users with health alerts before symptoms even appear.
8. Advanced Genomic Integration for Personalized Medicine
One of the most groundbreaking trends poised to revolutionize healthcare apps is genomic integration, which enables highly personalized treatment plans based on an individual’s genetic makeup. Genomics, the study of a person’s DNA and gene interactions, has seen incredible advances, and integrating this data into healthcare apps could unlock a new level of personalized medicine. Instead of the traditional one-size-fits-all approach, healthcare providers will be able to tailor treatment plans, medications, and preventive care based on a patient’s unique genetic profile.
This trend already shows immense potential in fields such as oncology, where genomic data is used to understand how certain cancers will respond to specific treatments. In the future, genomic integration into healthcare apps could extend to everyday care—helping patients identify the right medications, dietary plans, and even fitness regimens based on their genetic predispositions. As more patients access affordable genomic testing, healthcare apps that can interpret and apply this information will become invaluable. For example, apps could analyze genetic markers to predict a patient’s likelihood of developing conditions such as heart disease or Alzheimer’s, allowing for earlier interventions and lifestyle adjustments.
9. Biometric Authentication for Secure Health Data Access
As healthcare data becomes increasingly digitized and personalized, ensuring its security is paramount. Biometric authentication, which uses unique biological traits like fingerprints, facial recognition, or even retinal scans, is emerging as a robust method for securing sensitive health information within apps. Given the rise in healthcare data breaches, traditional passwords are no longer sufficient. To validate this, 2024 alone saw at least 14 million patients in the US getting affected by healthcare data breaches, with 91% involving ransomware attacks, states SonicWall. Thus, biometric authentication provides a higher level of security by using personal, hard-to-duplicate characteristics to ensure that only authorized individuals can access medical records and personal health data.
In the future, biometric technology is expected to become the standard for logging into healthcare apps, especially as mobile devices become more advanced. Beyond security, biometric authentication can improve user experience by offering fast, convenient access to important health data without the need to remember complex passwords. This is especially important for elderly patients or those with disabilities who may struggle with conventional security methods. Apple’s Face ID and Samsung’s fingerprint scanner are already integrated into some healthcare apps, but the next step would involve integrating more sophisticated biometrics such as voice recognition or heart rhythm analysis, ensuring not only secure access but also protecting the privacy of highly sensitive medical data.
10. Augmented Reality (AR) for Enhanced Diagnostics and Surgery
A forward-looking feature gaining traction in healthcare apps is Augmented Reality (AR). AR in healthcare apps allows doctors to overlay digital images, real-time data, or 3D models directly onto a patient’s body during procedures or examinations, providing enhanced visualization that aids in diagnostics, treatment planning, and surgery. This technology helps doctors better understand the patient’s anatomy, ensuring more precise and targeted interventions.
For example, surgeons can use AR-integrated apps to visualize complex structures like blood vessels or organs before making incisions, reducing the risk of errors during surgery. In diagnostics, AR can help doctors and specialists conduct more detailed examinations by overlaying information from CT scans, MRIs, or ultrasounds on the patient in real-time, leading to more accurate diagnoses and better treatment outcomes. In the future, AR combined with AI could offer predictive models during surgery or treatment planning, improving outcomes by providing real-time suggestions or warnings.
Related reading: Amp Up Your Lifestyle with Some Incredible Apps for Health and Fitness
6 Essential Factors for Developing mHealth App
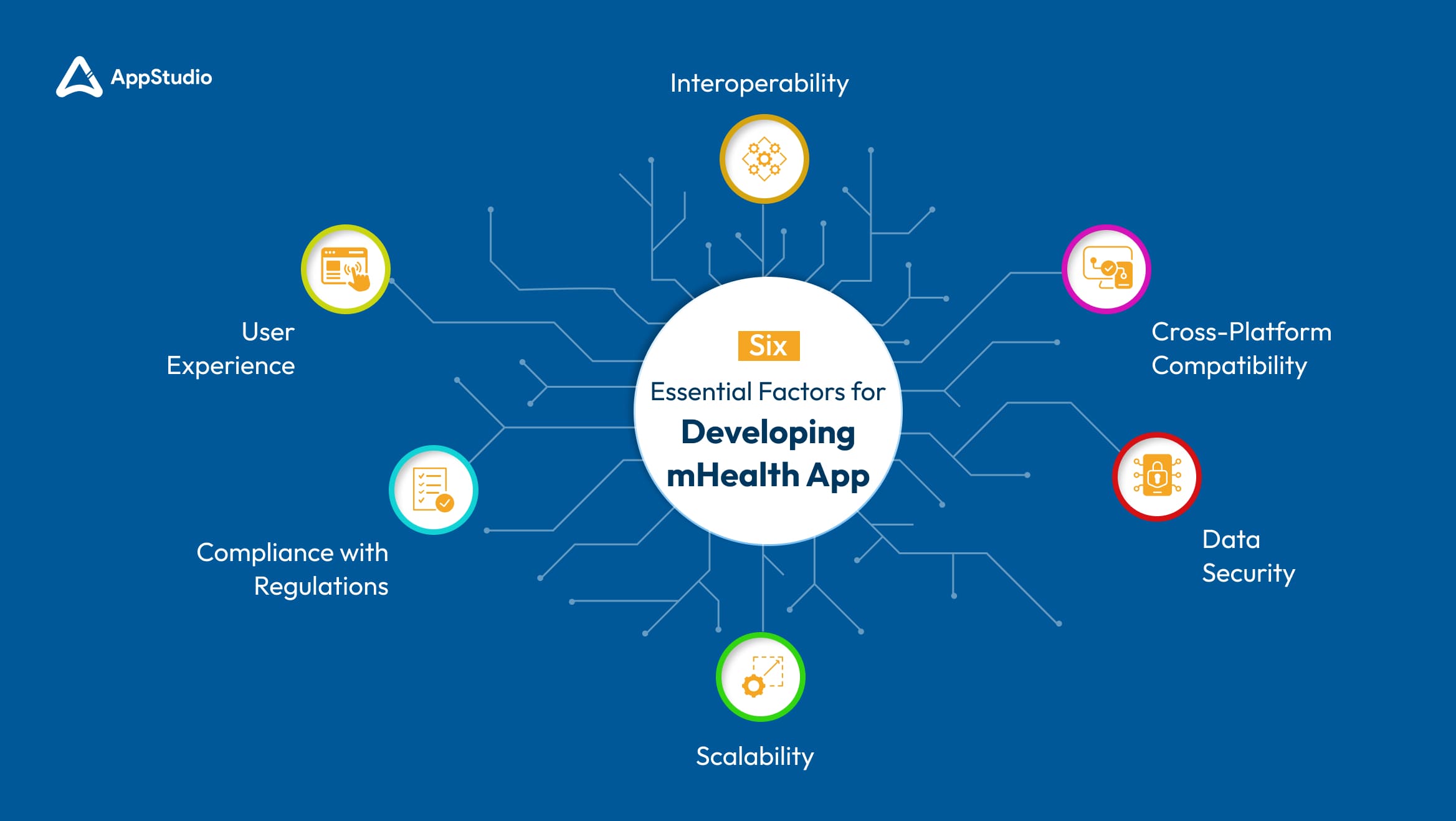
Developing healthcare mobile apps is not just about integrating trending features. Key factors must be considered to ensure the app is functional, secure, and scalable. Below are six critical considerations to focus on when developing a mHealth app.
1. Compliance with Regulations
What to Consider: One of the most important aspects of healthcare app development is regulatory compliance. Regulations like HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) in the US or GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) in Europe outline strict guidelines for handling sensitive patient data. These regulations mandate how data is collected, stored, and shared, ensuring patient privacy and the security of their health information.
Why It’s Important: Non-compliance can lead to hefty fines, legal repercussions, and a loss of trust from users. Beyond the financial and legal risks, protecting sensitive patient data is essential for maintaining ethical standards in healthcare.
2. User Experience
What to Consider: A seamless and intuitive user experience (UX) is critical for the success of any healthcare app. Both patients and healthcare professionals must be able to navigate the app easily, without frustration. Features like appointment scheduling, accessing medical records, and communication with healthcare providers should be simple and clear. The app’s design should cater to users of all tech-literacy levels, including older adults and less tech-savvy individuals.
Why It’s Important: A poor user experience can lead to decreased usage, low adoption rates, and negative reviews. In healthcare, where accessibility is key, a complicated interface can deter patients from using the app, potentially impacting their health outcomes.
3. Data Security
What to Consider: With healthcare apps handling a wealth of sensitive patient data, security must be a top priority. This means implementing robust encryption methods to protect data both at rest and in transit. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) should also be incorporated to ensure that only authorized users can access medical records and personal health data. Regular security audits and updates are necessary to keep up with evolving cyber threats.
Why It’s Important: In the wake of increasing cyberattacks targeting healthcare systems, strong data security measures are critical. Breaches not only lead to financial loss and legal liabilities but also damage the trust between patients and healthcare providers.
4. Interoperability
What to Consider: Interoperability refers to the app’s ability to work seamlessly with existing healthcare systems, such as Electronic Health Records (EHR) platforms and hospital information systems. The app should integrate with other platforms, allowing data sharing between various healthcare providers. This is especially important for large healthcare organizations that need to unify disparate systems to provide holistic care to patients.
Why It’s Important: Interoperability ensures that healthcare providers can access accurate, up-to-date patient information, which is critical for delivering timely and effective care.
5. Scalability
What to Consider: As your healthcare app grows in popularity, it must be able to handle increased traffic, data, and feature demands without compromising performance. A scalable architecture should be built from the start to ensure that as more users and healthcare providers adopt the app, it can continue to function smoothly. This includes server capacity, data storage, and the ability to easily add new features.
Why It’s Important: Without scalability, even the best-designed healthcare app will face performance issues as its user base expands. Slow load times, crashes, or data syncing problems will frustrate users, leading to high churn rates.
6. Cross-Platform Compatibility
What to Consider: In today’s time and age, users expect apps to work seamlessly across multiple platforms, particularly iOS and Android. Developing an app that offers a consistent experience on both operating systems ensures a wider user base and better adoption rates. Cross-platform development frameworks like Flutter or React Native can be leveraged to create apps that perform well on both platforms without doubling the development time or cost.
Why It’s Important: Reaching a broader audience is vital for the success of any mHealth app, and that can only happen if the app is compatible with all major platforms. Inconsistent performance between Android and iOS versions can lead to frustrated users and bad reviews.
Related reading: List of Best Health Apps to Integrate in Daily Routine
Conclusion
As the healthcare industry continues to evolve, so do the expectations for healthcare mobile apps. Both patients and healthcare professionals are seeking apps that are not only efficient but also secure, user-friendly, and innovative. In an era where convenience and personalization are at the forefront, the right blend of features can significantly enhance user experience while ensuring compliance and security. You can develop an app that meets these growing demands by incorporating essential healthcare app features—from telemedicine and AI-powered chatbots to advanced data security measures and seamless interoperability.To ensure your app is designed with these critical elements in mind, partnering with a trusted development team is crucial. At Appstudio, we are a world-class, industry-led app development company specializing in creating cutting-edge healthcare solutions tailored to the specific needs of healthcare professionals and patients like you. If you’re planning to develop a healthcare app, consider these key healthcare mobile app features to stay competitive and offer the best value to users while ensuring long-term success in this ever-evolving industry.
Frequently Asked Questions
Healthcare technology refers to the application of organized knowledge and skills in the form of devices, medicines, vaccines, procedures, and systems designed to solve health problems and improve quality of life.
They provide easy access to medical records, enable telemedicine consultations, send medication reminders, and allow for real-time health monitoring, improving patient engagement and outcomes.
Healthcare apps handle sensitive patient data, so encryption and multi-factor authentication are essential to protect against data breaches and maintain patient confidentiality.
Healthcare apps in the US must comply with HIPAA, which protects patient privacy and data security. If the app qualifies as a medical device, it must adhere to FDA regulations to ensure safety and effectiveness. Other relevant regulations include the HITECH Act and compliance with the FTC.
Telemedicine enables remote consultations, reducing the need for in-person visits and making healthcare more accessible, especially for those in remote areas or with mobility issues.
AI can be used to create chatbots that provide virtual assistance, offer personalized health recommendations, and analyze patient data to predict potential threats, health trends or complications.
Developers must prioritize compliance with healthcare regulations, ensure data security, provide an intuitive user experience, and design the app for scalability and cross-platform compatibility.