React Native is a cross-platform native application programming framework that is based on JavaScript and ReactJS. Created by technology giant Facebook, it has great benefits for businesses. Before we indulge in the advantages, have a look at our compilation of top 10 React Native development companies in Montreal.
Who is Behind This Technology?
Facebook is the main driver (an aspect that must also be taken into account and that can be given for another post about its implications) in principle, the sector has taken it as a guarantee. In addition, companies such as Instagram, Airbnb, Skype, Tesla or Uber (for Uber Eats) are already betting on this framework for their own applications.
To understand the impact that this technology can have on costs when developing an application for the iOS and Android platforms, it is important to remember that, until now, a native application with full quality and functionality required programming for each of its platforms. Objective-C or Swift for iOs and Java for Android, almost doubling the cost of production in the development and testing phases.
In React there is a “VirtualDOM“, in which we have our JSX, in which we define HTML documents, & these are transformed into browser components through JavaScript.
With React Native something similar happens, since we have our JSX components, which are going to be different from HTML components and will have other tags and other names, since we are not using HTML.
What is going to happen is that the compiler that has React Native will turn them into native elements of the interface for Android and iOS, which will allow these applications to have a look and feel similar to native applications, a performance practically the same and a navigation and user experience very similar to native applications, since what is being generated is a native interface.
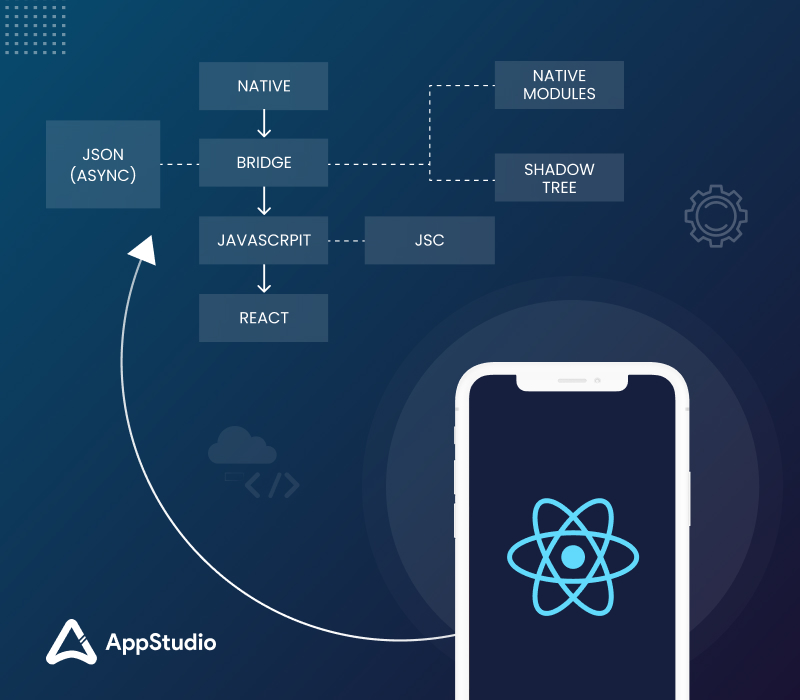
React Native Bridge
In addition to the above, JavaScript runs natively, does not compile or transpile to Java or ObjectiveC. This is because React Native is generating a kind of double thread, in which we have one running all the native code, all the part that continues to execute native modules such as the interface or any library that we have already integrated with Android programming in iOS , and on the other we have running a virtual machine running JavaScript.
The React Native Bridge is the one that will allow communication between both threads. It is different from the brige that we can have in converted HTML applications, which is what gives the functionality to native elements, since in this case it is this bridge that will communicate in JavaScript with the native part, for the passage of information or access of any device component.
In this way we will also achieve an execution performance, not only in the interface, close to the native one, and the deterioration part will be in the communication that we have to do between one part and the other.
There is Life After iOS and Android
Although it is normal to use React Native for Android and iOS, it does not only stay here, since we have more elements.
Not only is it the company itself that is developing these elements, but there are also third parties that are responsible for creating modules to run our React Native applications on the web.
Although it seems strange, there is a project called “React Native for Web”, which allows us to have our React Native components running in a browser.
There are other elements that allow us to use it in Windows or Mac desktop applications, or use it to create applications for Android or Apple smart watches, and also to run it on AppleTV and AndroidTV.
Although React Native is largely focused on mobile app development, you have to keep in mind that learning to work with it will allow you to work for other platforms and try to take more advantage of the part of code created.
And isn’t that What Hybrid Applications Did?
The answer is no. Hybrid applications (such as those developed with Cordova, Ionic, etc.) basically run web applications in app browsers. You could say that a web with app appearance was developed and it was executed in a container called Webview.
This technology, very useful for simple and ephemeral applications is, however, insufficient for applications that really need to use all the possibilities of mobile devices. We refer to services such as the camera, asynchronous notifications, gps, nfc, motion sensors, offline operation, etc. And the experience has never become as stable and fluid as an application developed in native code. For this reason, no application among the most downloaded of the marketplaces has been developed with hybrid technology.
Can You do Everything with React Native?
Logically one of the main doubts is what can be done and what not with React-Native, but the answer is a resounding yes. The development community for this platform does not stop growing and Facebook developers themselves do not stop publishing new native functionalities to expand the possibilities, however, another advantage of React Native is that, if necessary (a possible functionality or integration of a third-party service), it is possible to integrate native code into the project, so choosing React Native does not imply giving up the native code.